Sales tax in California: Rates, rules, and how to stay compliant
Sales tax in California affects every business transaction. Learn how to calculate rates, handle exemptions, and stay compliant.

Get the comprehensive guide
Learn the ins and outs of California sales tax, and how to stay compliant
Written by Kari Brummond—Content Writer, Accountant, IRS Enrolled Agent. Read Kari's full bio
Published Friday 7 November 2025
Table of contents
Key takeaways
• Register for a California sales tax permit through the CDTFA website for free, then file returns monthly if you collect over $1,000 per month in sales tax, quarterly for $601-$1,000, or annually for $600 or less per year.
• Calculate the correct sales tax rate by combining California's 7.25% base rate with local district taxes that can push total rates above 10% in some areas, using the CDTFA's official lookup tool to find your specific location's rate.
• Collect California sales tax if you have a physical presence in the state or reach $500,000 or more in yearly sales to California customers, regardless of where your business is located.
• Maintain detailed records of all sales transactions and file returns on time to avoid a 10% penalty plus interest on unpaid taxes, which the CDTFA actively enforces through audits and legal action.
California sales tax rates by county
California sales tax starts at 7.25% statewide but varies by location due to local district taxes. The total rate you charge customers depends on where your business operates.
California sales tax rates include a base rate and possible district taxes. Here’s how it works:
- Base statewide rate: 7.25% minimum (6% state + 1.25% local)
- Additional district taxes: 0.1% to 2% in some areas
- Maximum possible rate: Over 10% in certain jurisdictions
You must collect the combined rate for your location and report both state and local portions to the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA).
Charging the correct sales tax rate keeps your business compliant and helps you avoid penalties. Counties and cities may add district taxes, so total rates can go above 10% in some areas.
Charging the correct rate helps you avoid:
- undercollection penalties, such as fines and interest on unpaid amounts
- audit risks, including increased scrutiny from tax authorities
- customer disputes, such as refund requests for overcharging
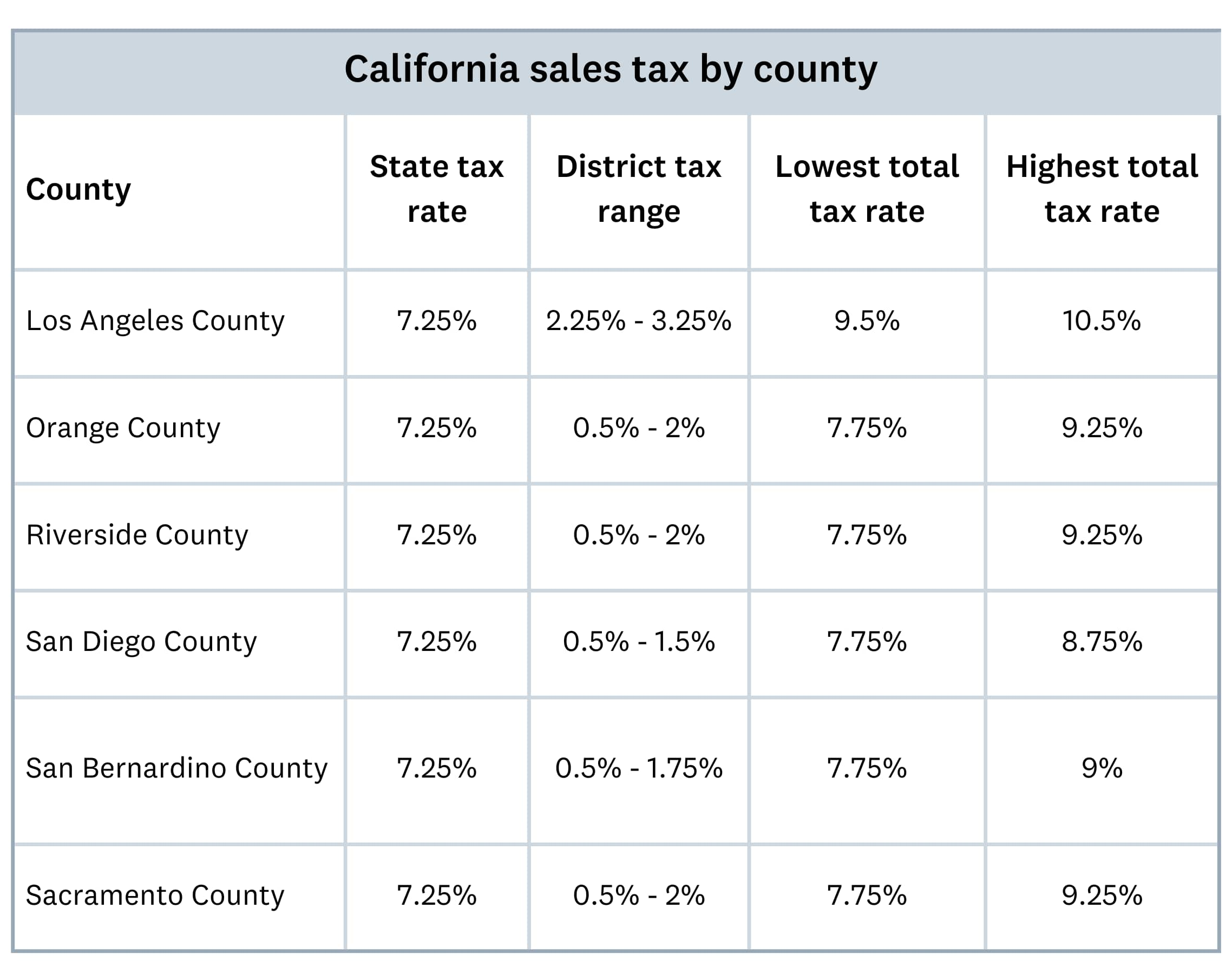
The table below provides a snapshot of how sales tax rates vary across different counties in California, based on additional district taxes:
For example, Los Angeles County has a district tax of 2.25%, so the minimum total tax rate is 9.5%. Some cities in the county may add more city taxes, so the total can be higher than 9.5%.
The California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA) provides an up-to-date breakdown of sales tax rates and fees by county and city. Use the official lookup tool to find the local rate for your business location.
How to calculate sales tax in California
California sales tax calculation uses a simple formula: tax rate × item price = sales tax amount. Add this amount to your product price to get the total cost for your customer.
Follow these steps to calculate sales tax in California:
- Convert rate to decimal: Divide by 100 (7.25% ÷ 100 = 0.0725)
- Multiply by item price: 0.0725 × $15.95 = $1.15 sales tax
- Add to item price: $15.95 + $1.15 = $17.10 total cost
For accurate local rates, use the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration lookup tool or automated tax calculation software.
How to register for a California sales tax permit
This applies to all business types, including sole proprietors, corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs).
You can register for your permit online through the CDTFA website. The process is free, but you may need to make a security deposit. You’ll need to provide information about your business, such as your social security number, bank details, and projected monthly sales.
California sales tax filing requirements
After registering, you'll need to file sales tax returns and remit the tax you've collected. The CDTFA will assign you a filing frequency based on your expected sales volume. This is typically monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Monthly: If you collect more than $1,000 per month in sales tax.
- Quarterly: If you collect between $601 and $1,000 per month.
- Annually: If you collect $600 or less per year.
File and pay on time to avoid penalties, such as a 10% fine on unpaid tax plus interest. Keep detailed records of your sales transactions to file accurately and on time.
Sales tax exemptions in California
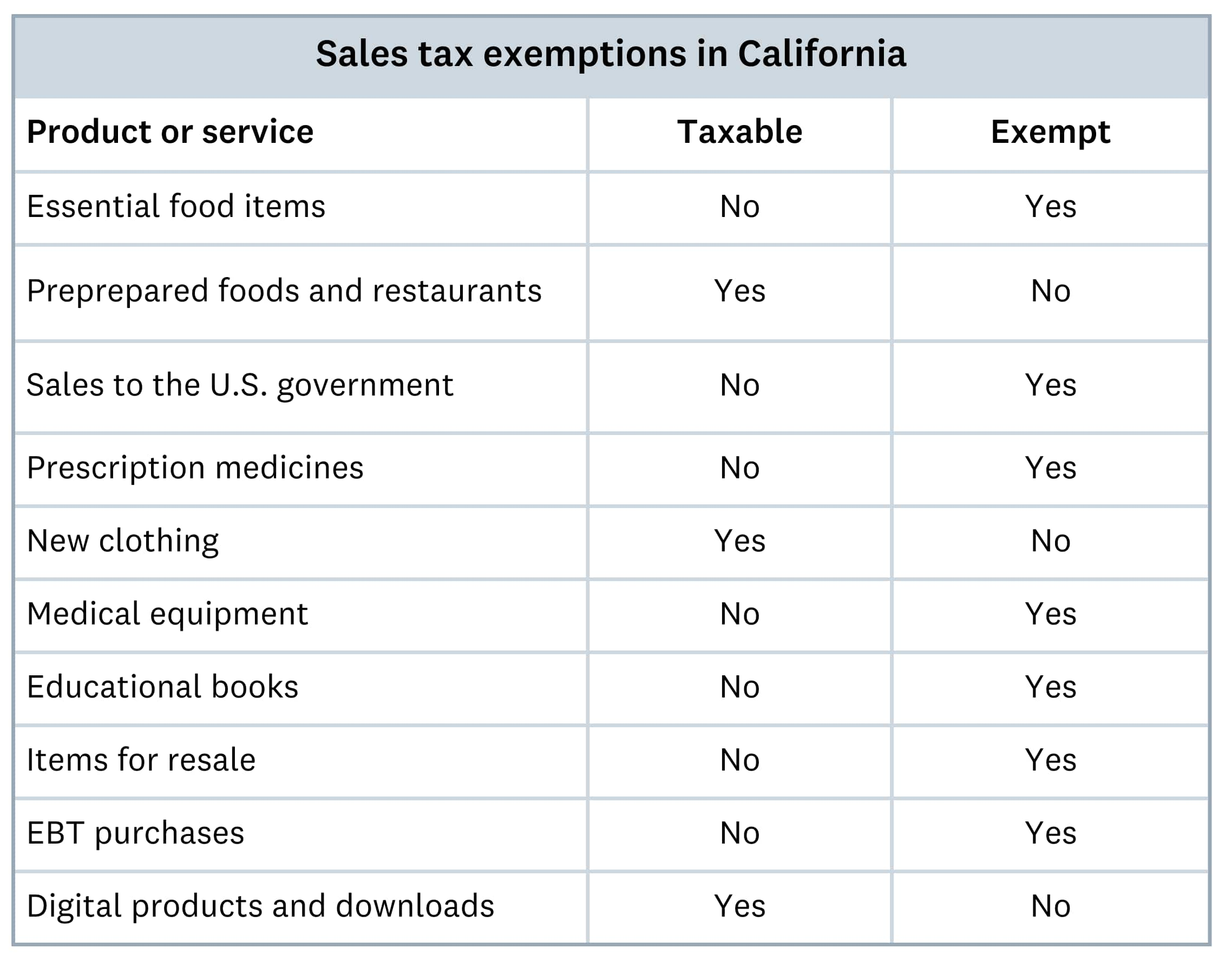
California sales tax exemptions apply to specific items and services that don’t require tax collection. Most tangible goods are taxable, but some exemptions help reduce your customers’ costs.
Commonly taxable items:
- Retail goods (clothing, electronics, furniture)
- Digital products and software
- Labor that creates tangible goods
Common exemptions include:
- Most unprepared food items
- Prescription medications
- Professional services (consulting, legal advice)
- Government services
A full list of nontaxable items can be found on the California Tax Service Center website.
Here's a comparison between some taxable and non-taxable products in California:
Online sales tax rules for California businesses
California online sales tax applies to businesses selling to California customers, regardless of your business location. The California Wayfair Law (AB147) requires tax collection based on economic nexus thresholds.
You’ll need to collect California sales tax if you meet any of these criteria:
- having a physical location in California, such as a store, warehouse, or office
- reaching $500,000 or more in yearly sales to California customers, even without a physical location
- selling through online platforms like Amazon, eBay, or Etsy, which collect and pay sales tax on your behalf
Compliance steps for online sellers
If you sell online to California residents, make sure you collect and pay sales tax correctly. Follow these steps to stay compliant:
- Register for a California seller’s permit through the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA).
- Collect the correct tax rate for state, county, city, and district taxes (7.25% plus local district taxes). Use a California state tax calculator to make sure you apply the right rate.
- File and pay sales tax on your assigned schedule. Some businesses file quarterly, while others file bi-annually or annually.
- Keep detailed records of your sales transactions for tax audits.
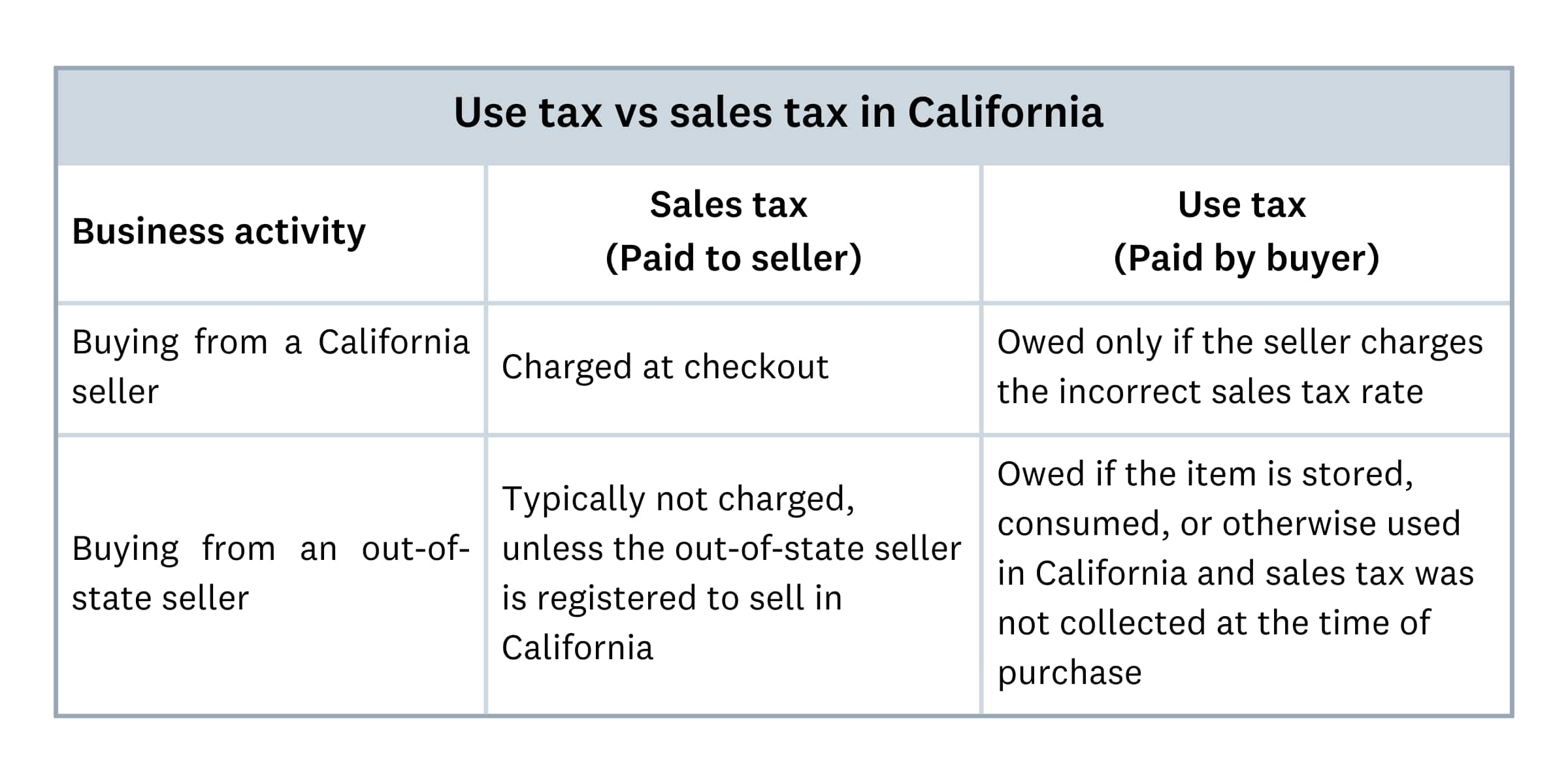
Use tax vs. sales tax in California
California use tax is the buyer’s responsibility when sales tax wasn’t collected at purchase. Sales tax is collected by sellers and sent to the state. Knowing the difference helps you stay compliant.
Key differences:
- sales tax, which the seller collects and pays to the CDTFA
- use tax, which the buyer pays directly to the CDTFA
- the same rate applies to both taxes
When does use tax apply?
You’ll need to pay use tax in these situations:
- buying from vendors who don’t collect California tax
- purchasing from sellers without California tax obligations
- buying items tax-free but using them in California
- importing goods directly from manufacturers or foreign suppliers
Here's a breakdown of how use tax and sales tax work:
Use a California sales tax calculator to make sure you apply the correct rates for each transaction.
Simplify your California sales tax management with Xero
California’s sales tax rates, filing deadlines, and rules can be complex. Xero accounting software simplifies sales tax by automatically calculating rates on your invoices and tracking what you owe, so you can file your returns with confidence.
When you connect your business finances in one place, you get a clear view of your tax obligations. Spend less time on bookkeeping and more time running your business. Try Xero accounting software to manage sales tax easily and get one month free.
Frequently asked questions about California sales tax
What happens if a business doesn't collect or remit sales tax in California?
If you don’t collect or pay sales tax, you could face a 10% fine plus interest on unpaid taxes. The CDTFA may also take legal action or audit your business.
Is labor subject to sales tax in California?
It depends on the type of labor. Physical labor that creates a tangible product, like car repairs, furniture assembly, or appliance installation, is taxable. Professional services, such as healthcare, consulting, or legal advice, aren’t taxable. See the CDTFA website for more information on what type of labor is subject to sales tax.
Do nonprofit organizations have to pay California sales tax?
Yes. Most nonprofits must pay sales tax unless they have tax-exempt status from the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA). Exempt organizations include charities, cultural groups like libraries and museums, veterans’ groups, religious organizations, and educational organizations. If your business is a nonprofit, check with the CDTFA to confirm your exemption before selling.
Is there a sales tax on real estate transactions in California?
No, real estate sales aren’t subject to sales tax in California. But a leased commercial property may be subject to local district taxes, depending on the lease terms. For example, if you lease a warehouse to store products you sell online, you may need to pay local district taxes.
Does California charge sales tax on vehicle purchases?
Yes. If you buy a car in California, you’ll pay the state’s base sales tax rate of 7.25%, plus any local district taxes. If you buy from a private seller, you’ll need to report and pay the tax when you register the vehicle with the California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV).
How does California's sales tax apply to shipping and delivery charges?
If shipping charges are separate from the item’s price, they’re not taxable. But if shipping is bundled into the total price, or if you can’t arrange your own shipping, then the shipping charges are taxable. Read more on the CDTFA website.
Are digital goods and software subject to California sales tax?
Most digital goods, like eBooks, online courses, and streaming services, aren’t subject to sales tax. But prepackaged software you download or keep on physical media is taxable.
Does California offer sales tax holidays?
No, California doesn’t have sales tax holidays. Some states temporarily exempt specific items, but California doesn’t offer these holidays.
Get one month free
Sign up to any Xero plan, and we will give you the first month free.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.