How to calculate profitability: formulas, margins and tips
Learn how to calculate profitability, track what drives your profit, and make smarter pricing and cost decisions.
Written by Lena Hanna—Trusted CPA Guidance on Accounting and Tax. Read Lena's full bio
Published Monday 12 January 2026
Table of contents
Key takeaways
- Calculate both gross profit margin (revenue minus cost of sales divided by revenue) and net profit margin (revenue minus all expenses divided by revenue) to understand how efficiently your business converts sales into profits at different levels.
- Monitor your profitability margins monthly and immediately when costs change to spot cash flow issues early and maintain financial flexibility for unexpected expenses.
- Use accounting software like Xero to automate profitability calculations and access real-time dashboards that show margin trends, eliminating manual calculations and providing instant visibility into your financial performance.
- Improve low margins by increasing prices, reducing cost of sales through better suppliers or efficiency improvements, or cutting operating expenses like rent and utilities.
What profitability means in small business
Profitability measures how efficiently your business converts sales revenue into profits. This efficiency is a key component in broader financial analysis, as metrics like operating profit margin are used to calculate performance indicators like return on capital employed (ROCE).
The two main profitability metrics are:
- Gross profit margin: Shows what percentage of revenue remains after paying direct costs
- Net profit margin: Shows what percentage of revenue remains after paying all business expenses
These metrics tell you exactly how much of every pound in sales you get to keep versus what goes back out to cover costs.
High profitability (fat margins): You keep a large portion of sales revenue as profit. This gives you financial flexibility, but it may also mean you could lower prices to increase sales volume.
Low profitability (thin margins): Most revenue goes to covering expenses. This typically indicates:
- Operating costs are too high
- Pricing is too low for your market
- You're competing primarily on price rather than value
The difference between profit and profitability
- Profit is the amount of money your business makes after paying its expenses.
- Profitability is the percentage of revenue you get to keep (vs the percentage that you spend to operate the business).
It's an important distinction. High profitability only boosts your bottom line if it's coupled with good revenue. So you want good profitability and good sales.
Profitability metrics
The most common profitability metrics are your gross and net profit margins. These are sometimes referred to as profitability ratios.
Gross profit margin
Gross profit margin measures the percentage of revenue left after paying costs of sales (direct costs of producing your goods or services).
Why it matters: Your gross profit covers operating expenses like rent, utilities, marketing, and administration. A higher gross margin gives you more money to run your business and still generate net profit.
Net profit margin
Net profit margin measures the percentage of revenue remaining after paying all business expenses.
Why it matters: Net profit is what you actually keep from sales. This money can be reinvested in business growth or distributed to owners as profit.
Businesses may quote net profit before taxes, or after taxes. In this context, you can treat net profit as profit before taxes.
How to measure profitability
Profitability calculation follows this basic formula: (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100 = Profitability percentage.
The key difference is which profit figure you use:
- Gross profit margin: Use gross profit (revenue minus cost of sales)
- Net profit margin: Use net profit (revenue minus all expenses)
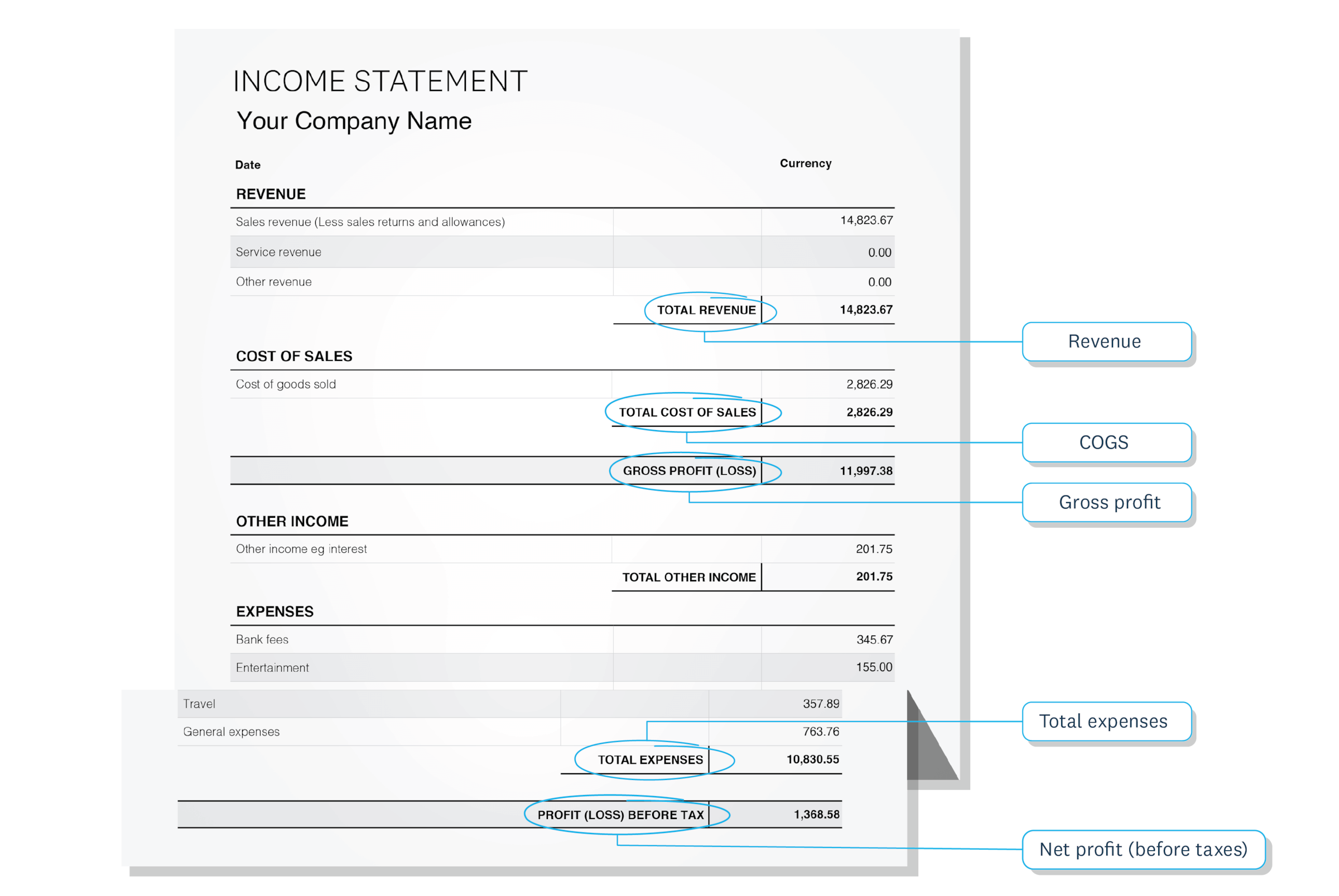
How to measure gross profit margin
Use the Xero gross margin calculator to work this out.
How to measure net profit margin
Use the Xero net profit margin calculator to check your margin.
*Net profit can be quoted before or after taxes. If quoting after-tax net profit then you need to also subtract taxes.
*Net profit can be quoted before or after taxes. For the examples in this guide, use net profit before taxes. If you quote after-tax net profit, subtract taxes as well.
Example of profitability measurement
Example calculation for a business with £100,000 revenue, £60,000 cost of sales, and £20,000 operating expenses:
Step 1: Calculate gross profit£100K revenue - £60K cost of sales = £40K gross profit
Step 2: Calculate gross profit margin(£40K ÷ £100K) × 100 = 40% gross profit margin
Step 3: Calculate net profit£100K revenue - £80K total expenses = £20K net profit
Step 4: Calculate net profit margin(£20K ÷ £100K) × 100 = 20% net profit margin
How to measure profitability with software
Accounting software automates profitability calculations and eliminates manual work. With Xero accounting software, you can:
- View instant margins: Access Xero Analytics and select your measurement period
- Generate reports: Create profit and loss statements that show your margins automatically
- Track trends: Monitor profitability changes over time with real-time dashboards
Why it's important to keep measuring profitability
Regular profitability measurement prevents cash flow problems and reduces business stress. When margins shrink, you face:
- Cash flow issues: Less profit means less money to cover expenses; for instance, accountants use an 'interest cover' ratio to assess if a company's profits are high enough to safely meet its interest payments
- Increased pressure: Tight margins leave no room for unexpected costs
- Difficult decisions: You must balance competitive pricing with sustainable profits
Monitor profitability regularly because margins change due to:
- Cost fluctuations: Raw materials, energy, transport, and rent increases
- Market conditions: Interest rates, exchange rates, and competitive pressure
- Business growth: New expenses and changing customer demands
Regular measurement ensures you maintain healthy margins and spot problems early.
How to manage profitability
Managing profitability requires consistent monitoring and clear benchmarks:
When to measure:
- Monthly for trend tracking
- Immediately when costs change
- During competitive pricing pressures
How to set targets:
- Establish your preferred margin as a benchmark
- Consult industry-specific accountants for sector norms, as benchmarks for financial health, like the current ratio, can vary between industry sectors
- Adjust targets based on business goals and market conditions
Improve low margins using these strategies:
- Increase prices: Raise rates for products or services
- Reduce cost of sales: Find cheaper suppliers or improve efficiency
- Cut operating expenses: Lower rent, utilities, or administrative costs
For detailed strategies, see the guide on how to increase profits.
Taking control of your business profitability
Understanding and measuring profitability is more than just a numbers game; it gives you the clarity and confidence to steer your business towards success. By regularly tracking your margins, you can make smarter decisions, spot opportunities, and build a more resilient business.
Ready to run your business, not your books? Try Xero for free and see how easy it is to get real-time insights into your profitability.
FAQs on measuring profitability
Here are answers to some common questions about measuring profitability.
What are the main formulas for profitability?
The two key formulas are for gross and net profit margins. For gross profit margin, you divide your gross profit by revenue. For net profit margin, you divide your net profit by revenue. Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage.
What's the difference between profit and profitability?
Profit is a fixed number: the total money left after subtracting expenses from revenue. Profitability is a percentage that shows how efficiently your business turns revenue into profit. A business can have high profit but low profitability if it needs massive sales to make that profit.
How often should I measure profitability?
It's a good practice to review your profitability monthly. This allows you to react quickly to changes in costs or sales. You should also measure it any time you make significant changes to your pricing, suppliers, or general expenses.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.
Start using Xero for free
Access Xero features for 30 days, then decide which plan best suits your business.