How to calculate profitability: formulas, metrics, and examples
Learn how to calculate profitability, track margins, and spot actions to cut costs and grow with confidence.
Written by Lena Hanna—Trusted CPA Guidance on Accounting and Tax. Read Lena's full bio
Published Tuesday 27 January 2026
Table of contents
Key takeaways
- Calculate both gross profit margin (revenue minus direct costs divided by revenue) and net profit margin (revenue minus all expenses divided by revenue) to understand different aspects of your business efficiency and overall profitability.
- Track your profitability metrics monthly for regular monitoring and immediately when costs change significantly, focusing on trends rather than daily fluctuations to make informed business decisions.
- Use accounting software to automate profitability calculations and access real-time metrics, which eliminates manual errors and provides instant access to profit and loss statements for any period.
- Compare your profit margins against industry benchmarks from sources like the Australian Taxation Office to determine if your business performance is competitive and identify areas for improvement.
What profitability means in small business
Profitability measures how efficiently your business converts sales into profits. It shows what percentage of revenue remains after covering costs.
The two main profitability metrics are:
- Gross profit margin is the percentage of revenue left after direct costs.
- Net profit margin is the percentage of revenue left after all expenses.
High profitability (fat margins):
- Keep large percentage of sales revenue as profit
- May indicate prices could be lowered to increase sales volume
Low profitability (thin margins):
- Most revenue goes toward covering expenses
- May indicate high costs, low pricing, or competitive pressure
Profit vs profitability and their significant differences
- Profit is the dollar amount left after paying expenses.
- Profitability is the percentage of revenue you keep after covering costs.
It's an important distinction. High profitability only boosts your bottom line if it's coupled with good revenue. So you want good profitability and good sales.
Profitability metrics
Profitability metrics measure different aspects of your business efficiency. The two essential metrics are:
- Gross profit margin: Measures efficiency after direct costs
- Net profit margin: Measures overall business efficiency
You might also hear these metrics called profitability ratios.
Gross profit margin
Gross profit margin measures the percentage of revenue left after paying direct costs of goods sold (COGS). This figure varies by industry; for example, the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) benchmark range for 'cost of sales' for footwear retailers is 48% to 59% of turnover.
This remaining money covers general expenses like:
- Rent and utilities
- Marketing and insurance
- Administration costs
- Staff salaries, which can significantly impact profitability. In one case study, a business's salary expenses were 53.2% of sales, more than double the industry benchmark of 20 to 25%.
Net profit margin
Net profit margin measures the percentage of revenue remaining after paying all business expenses. The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) uses data from tax returns to calculate this ratio for industry benchmarks, defining it as total business income minus total expenses, divided by total business income.
Why it matters: This is the money you keep to reinvest in growth or distribute to owners.
Businesses may quote net profit before taxes, or after taxes. In this guide, you focus on net profit before taxes.
How to calculate profitability
Profitability calculation follows this basic formula: (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100 = Profitability percentage.
The calculation process:
- Determine your profit amount (gross or net)
- Divide profit by total revenue
- Multiply result by 100 for percentage
How to calculate gross profit margin
You can use the Xero margin calculator.
How to calculate net profit margin
*Net profit can be quoted before or after taxes. If quoting after-tax net profit then you need to also subtract taxes.
You can use the Xero net profit margin calculator.
Example of profitability calculation
Example calculation for a business with $100K revenue, $60K inventory costs, $20K general expenses:
Step 1 - Calculate gross profit:$100K revenue - $60K cost of goods sold = $40K gross profit
Step 2 - Calculate gross profit margin:($40K ÷ $100K) × 100 = 40% gross profit margin
Step 3 - Calculate net profit:$100K revenue - $80K total costs = $20K net profit
Step 4 - Calculate net profit margin:($20K ÷ $100K) × 100 = 20% net profit margin
Finding the numbers to calculate profitability
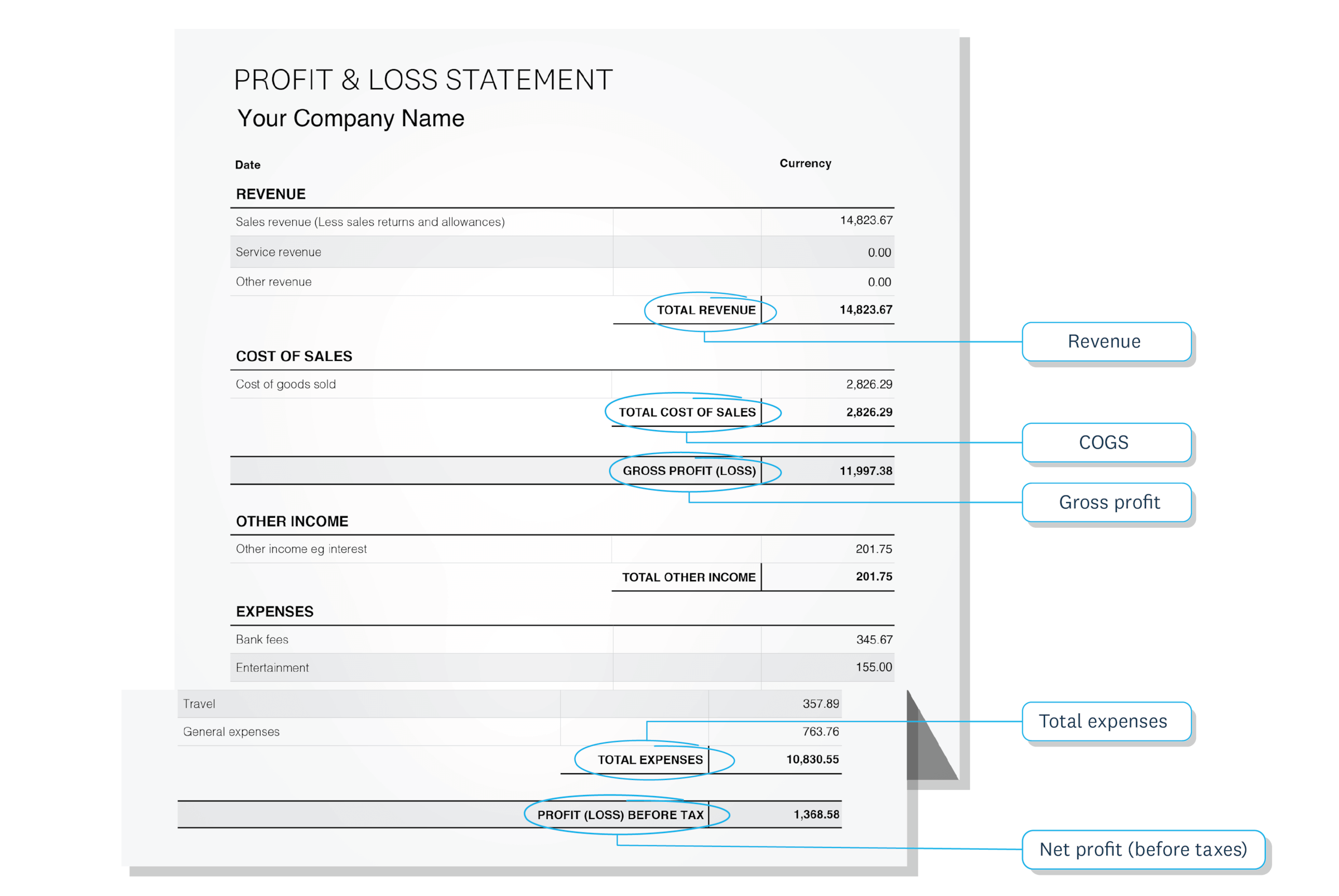
To calculate profitability, you first need to gather specific financial data from your business records.
- Revenue numbers: Found in your sales reports or income statements
- Cost of goods sold: Listed in your expense tracking or inventory records
- Total expenses: Available in your profit and loss statements
How to calculate profitability with software
Accounting software automates profitability calculations, eliminating manual maths and reducing errors. With Xero accounting software, you can:
- Access pre-calculated margins in Xero Analytics
- Generate profit and loss statements for any period
- View real-time profitability metrics automatically
Why it's important to keep calculating profitability
Regularly measuring profitability helps protect your business health and your wellbeing.
Why margins matter:
- Wider margins improve cash flow and help reduce stress
- Healthy margins provide financial breathing space
- Balance needed between profitability and customer value
Factors that affect margins:
- Raw material costs
- Energy and transport expenses
- Interest rates and rent increases
- Exchange rate fluctuations
Keep your profitability calculations simple
Keep your profitability calculations simple by focusing on the metrics that matter most to your business.
Start with the basics:
- Track gross and net profit margins monthly
- Use consistent calculation periods (monthly or quarterly)
- Focus on trends rather than daily fluctuations
Keep things simple:
- Focus on a few key ratios at first
- Use accounting software for automatic calculations
- Review quarterly rather than obsessing over daily changes
Simple tracking delivers better results than complex systems you won't maintain consistently. Try Xero for free to automate your accounting and track your profitability with ease.
FAQs on calculating profitability
Common questions about measuring your business profitability.
What are the main profitability ratios I should calculate?
Gross profit margin and net profit margin are the essential ratios for most small businesses. Gross margin shows efficiency after direct costs, while net margin reveals overall business profitability.
How often should I calculate my business profitability?
Calculate profitability monthly for regular monitoring and immediately when costs change significantly. Quarterly reviews help identify trends without daily fluctuation distractions.
What's considered a good profit margin for a small business?
Good margins vary by industry. While general guidelines suggest a 10–20% net profit margin for most small businesses, specific benchmarks differ. For example, the ATO's key benchmark range for total expenses for plumbing businesses with over $600,000 turnover is 76% to 87%, which implies a net profit margin of 13% to 24%. Consult industry-specific accountants for accurate benchmarks in your sector.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.
Start using Xero for free
Access Xero features for 30 days, then decide which plan best suits your business.