Sales tax in Texas: Rates, exemptions and how to stay compliant
Sales tax in Texas varies by location and affects every business transaction. Learn how to calculate the right rates and stay compliant.

Written by Kari Brummond—Content Writer, Accountant, IRS Enrolled Agent. Read Kari's full bio
Published Friday 7 November 2025
Table of contents
Key takeaways
• Register for a Texas sales tax permit before collecting any sales tax and determine your filing frequency (monthly, quarterly, or annually) based on how much tax you collect.
• Calculate sales tax by multiplying your combined local rate (6.25% state plus up to 2% local, maximum 8.25%) by the item price, then round to the nearest penny.
• Recognize that online businesses must collect Texas sales tax if they exceed $500,000 in Texas sales within the previous 12 months, regardless of physical presence in the state.
• Apply use tax when you purchase taxable items for your business without paying sales tax at the time of purchase, such as out-of-state purchases or tax-free items used in Texas.
Key takeaways
- Texas charges a 6.25% state sales tax, with local jurisdictions able to add up to 2%, for a maximum of 8.25%.
- Sales tax applies to most goods and some services, but exemptions exist for items like groceries, prescription drugs, and certain medical devices.
- Multiply the tax rate by the item price and round correctly to calculate sales tax
- Businesses selling online in Texas – regardless of physical presence – must collect and remit sales tax if they meet economic thresholds
- Staying compliant includes registering for a tax permit, collecting and filing sales tax properly, and maintaining transaction records. Use tax may apply when Texas sales tax isn't collected at the time of purchase.
- Texas offers sales tax holidays for specific items at certain times of year.
- Failing to collect or remit tax can result in penalties, audits, and interest charges.
How much is sales tax in Texas?
Texas sales tax is a 6.25% state tax imposed on most retail sales, leases, and rentals of goods and taxable services. Local jurisdictions can add up to 2% more, creating a maximum combined rate of 8.25%.
.1744351186849.png)
Understanding these rates helps you collect the right amount from customers and stay compliant.
Texas sales tax rates by location
Local sales tax rates vary by jurisdiction and can add up to 2% to the state rate. This creates combined rates ranging from 6.25% to 8.25% across Texas.
Local sales tax rates can vary. Here are some key points to know:
- Cities and counties can each impose additional taxes
- Maximum total: 8.25% (6.25% state + 2% local)
- Rate verification: Check the Texas Comptroller website for current rates in your area
The table below shows tax rates in several Texas cities.
.1744351186849.png)
Check the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts website for the latest local sales tax rates.
How to calculate Texas sales tax
To calculate Texas sales tax, multiply your local tax rate by the item price.
Basic formula: Sales tax = tax rate × item price
Follow these steps to calculate Texas sales tax:
- Find your local rate: Combine state (6.25%) + local taxes
- Convert to decimal: Divide rate by 100 (8.25% = 0.0825)
- Calculate tax: Multiply item price by decimal rate
- Round correctly: Round to nearest penny
Find your local sales tax rates on the Texas sales tax page.
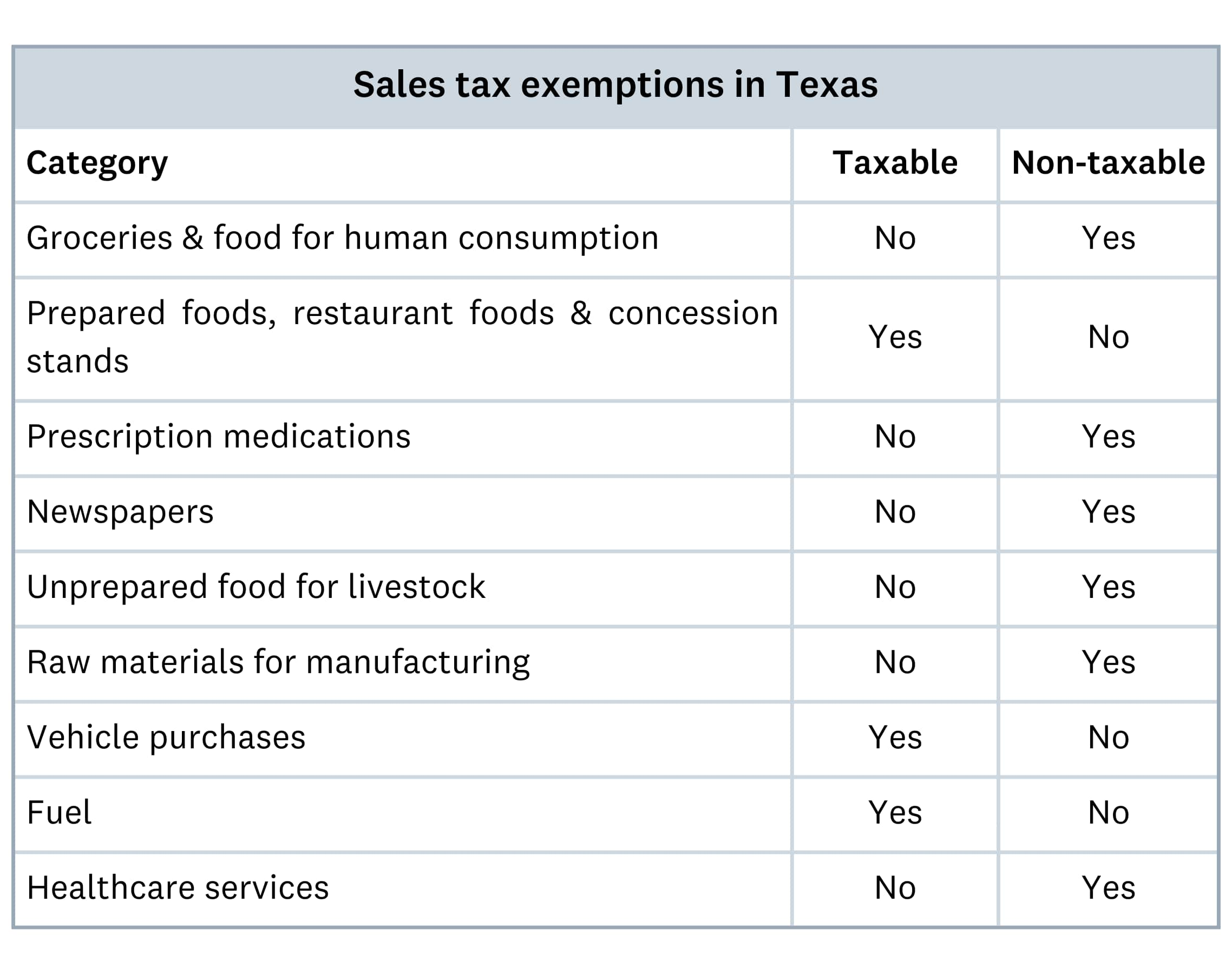
Sales tax exemptions in Texas
Some items and services are exempt from Texas sales tax. The table below shows common exemptions:
Some items and services are exempt from Texas sales tax. Knowing these exemptions helps you charge customers correctly and stay compliant.
Common exempt items:
- Food products such as meat, fruits, vegetables, and other groceries
- Medical items: Prescription drugs and certain medical devices
- Services: Most professional services like legal and medical advice
- Manufacturing: Items used directly in manufacturing processes
How to register for a Texas sales tax permit
Register with the state to collect sales tax. Apply for your Texas sales tax permit online to operate your business legally.
Follow these steps to get your permit:
- Gather your information: You'll need your Social Security number, business entity details, and North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) code.
- Complete the application: Visit the Texas Comptroller's eSystems website to fill out the application for a sales tax permit.
- Receive your permit: Once your application is approved, you'll receive your permit and be assigned a filing frequency.
Filing schedules and due dates
Your filing schedule depends on how much sales tax you collect. The Texas Comptroller assigns your filing frequency when you register for your permit.
Your filing schedule could be:
- Monthly: If you owe more than $1,500 in state tax per quarter.
- Quarterly: If you owe less than $1,500 in state tax per quarter.
- Annually: If you owe less than $1,000 in state tax per year.
Returns are generally due on the 20 day of the month after the reporting period ends.
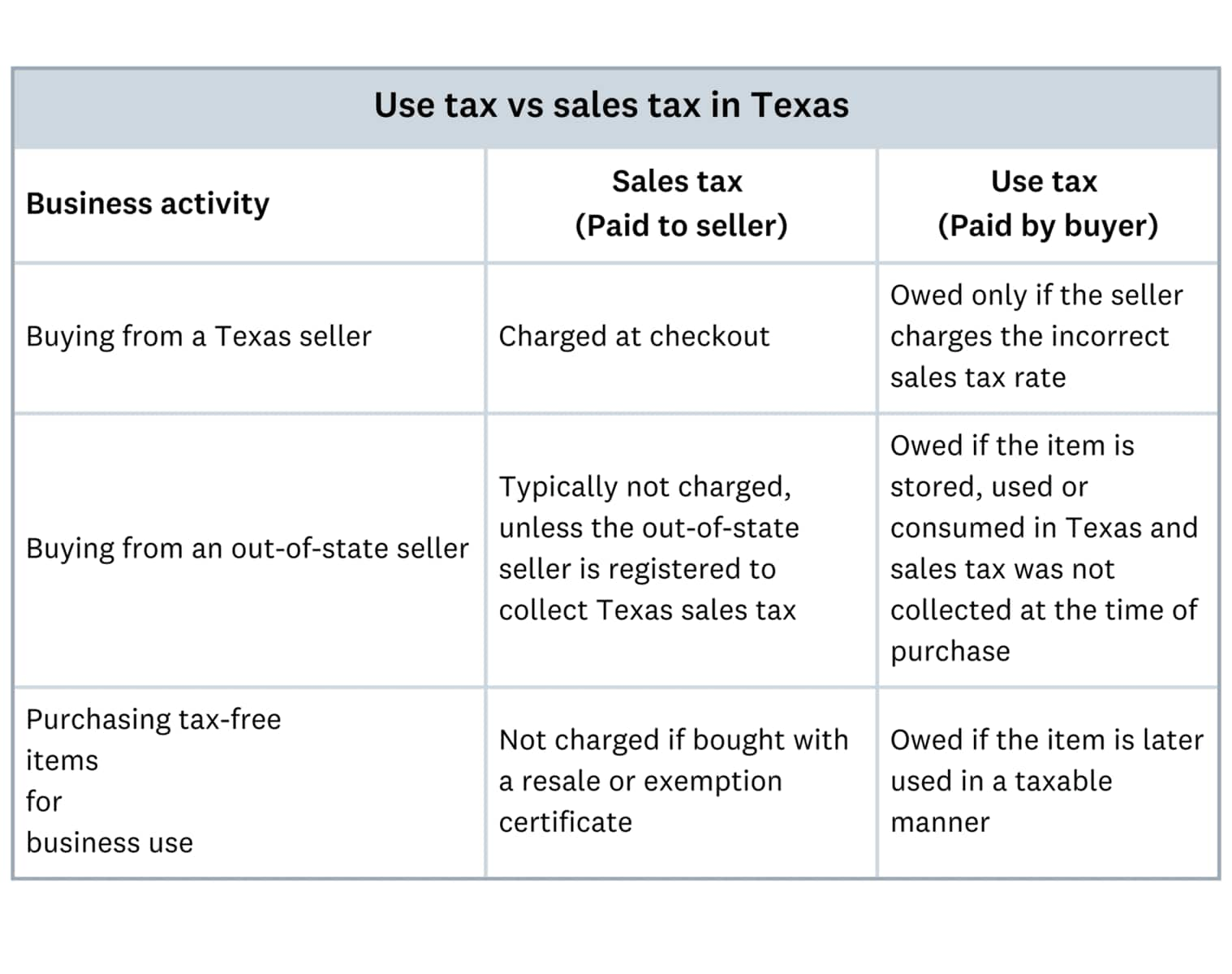
Use tax vs. sales tax in Texas
You pay use tax on taxable items you use, store, or consume in Texas if you did not pay sales tax at the time of purchase.
Key differences:
- Sales tax: Collected by seller at purchase
- Use tax: Paid by buyer when sales tax wasn't collected
- Same rate: Both use identical tax rates
- Payment: Made directly to Texas Comptroller
Use tax applies to:
- out-of-state purchases where Texas sales tax isn't collected
- online transactions from sellers who don't collect sales tax
- tax-free purchases that are used in Texas
- purchases of taxable items in another country or state that are brought to Texas
For instance, if you purchase office equipment online from a seller that doesn't charge sales tax, you must report and pay use tax directly to the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts. Similarly, a Texas business that purchases manufacturing materials tax-free from an out-of-state vendor but uses the materials in Texas must pay use tax.
Knowing when use tax applies helps you stay organized and manage your business finances.
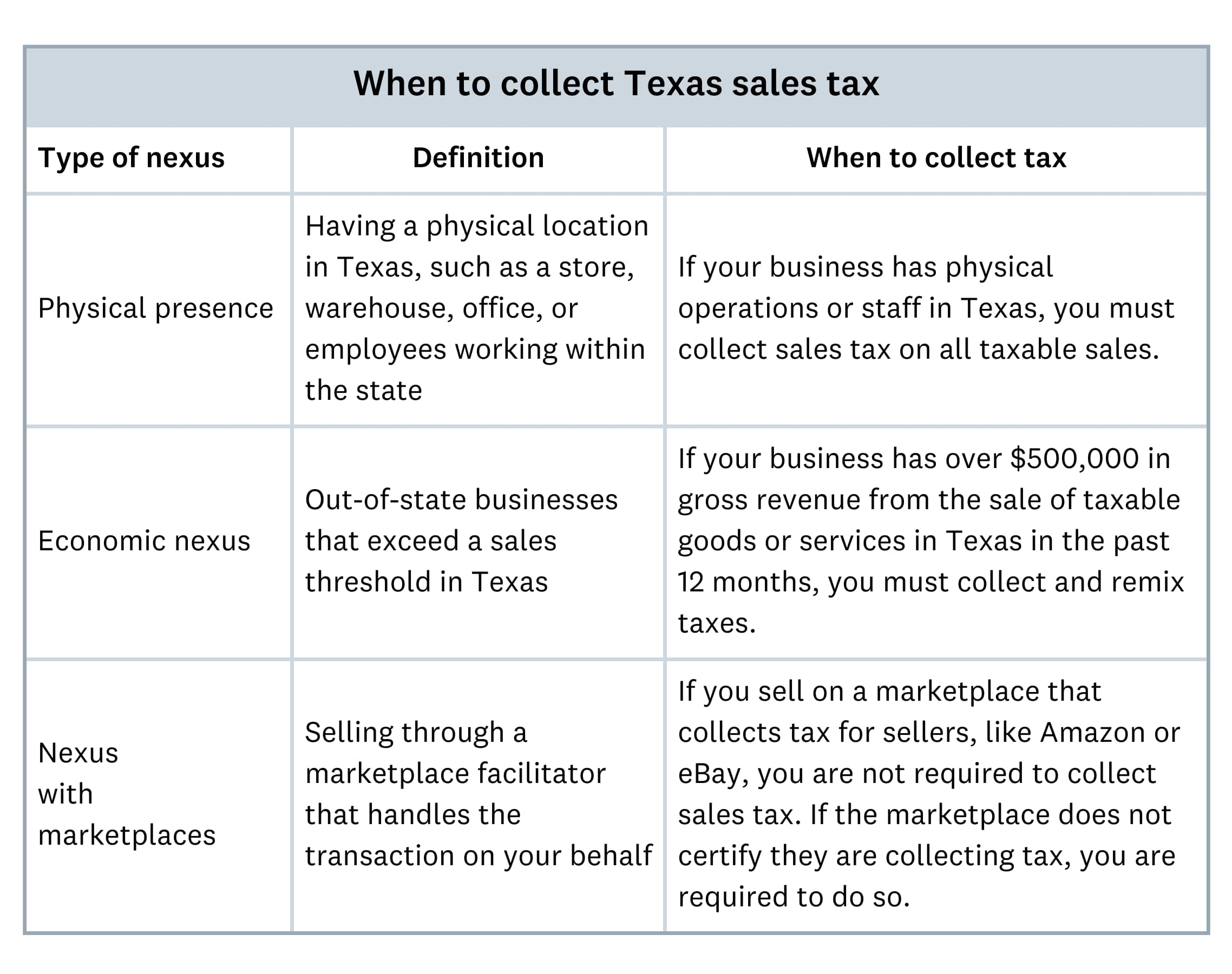
Online sales tax rules for Texas businesses
Remote sellers must collect Texas sales tax if they exceed certain sales thresholds, even if they do not have a physical presence in the state. All 45 states with a statewide sales tax have adopted requirements for remote sellers.
Texas Wayfair Law requirements:
- Effective date: October 1, 2019
- Sales threshold: $500,000 in Texas sales in the previous 12 months
- Tax collection: State rate (6.25%) plus applicable local taxes
- Who must comply: Remote sellers and online marketplaces meeting thresholds; these remote sales represent a major revenue stream, with 33 states reporting 2021 collections totaling around $23.1 billion.
Penalties for non-compliance
Stay on top of your sales tax obligations to keep your business in good standing. The Texas Comptroller can impose penalties if you do not collect or remit tax on time.
Penalties include a 5 percent fee for late filing and an additional 5 percent if you are more than 30 days late. Interest applies to unpaid tax. File and pay on time to keep your business in good standing.
Manage your Texas sales tax with confidence
You can manage Texas sales tax easily with the right tools and knowledge. Xero gives you a real-time view of your finances so you can make smarter decisions and focus on running your business.
Try Xero free for one month and see how it can help your business.
FAQs on Texas sales tax
You may have questions about Texas sales tax. Here are answers to some common questions.
Do you need a sales tax permit in Texas?
Yes. You must register for a Texas sales tax permit with the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts before you collect sales tax.
How often do you need to file Texas sales tax returns?
Your filing frequency depends on how much sales tax you collect. The Texas Comptroller assigns your schedule: monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Is labor subject to sales tax in Texas?
It depends on the type of labor. Labor that creates a taxable product – such as furniture assembly or appliance installation – is subject to sales tax. Professional services like legal advice, medical services, and consulting are exempt. Some repair and remodeling services for nonresidential property may be taxable. Check the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts for details.
Do nonprofit organizations have to pay Texas sales tax?
Most nonprofit organizations in Texas must pay sales tax unless they have tax-exempt status from the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts. To qualify, you must meet certain criteria and get a Texas sales tax exemption certificate. Some purchases and sales by qualifying nonprofits may be exempt, depending on your organization and activities.
Is there a sales tax on real estate transactions in Texas?
No. Real estate sales are not subject to sales tax in Texas. Some commercial property leases may be taxable, depending on the lease terms. Real estate transactions may also have other taxes and fees, such as property taxes and documentary transfer taxes.
Does Texas charge sales tax on vehicle purchases?
Yes. Vehicles purchased in Texas are subject to a 6.25 percent motor vehicle sales tax. This applies to purchases from dealerships and private sellers. If you buy from a private seller, you must report and pay the tax when you register the vehicle with the Texas Department of Motor Vehicles (TxDMV). Local sales taxes do not apply to vehicle purchases.
How does Texas's sales tax apply to shipping and delivery charges?
In Texas, shipping and delivery charges are taxable if the item is taxable. If the purchase is exempt, the shipping charge is also exempt. If the seller includes shipping in the total price or does not let you arrange your own shipping, the delivery charge is taxable. If shipping is listed separately and the item is not taxable, the shipping charge is not taxed.
Does Texas offer sales tax holidays?
Yes. Texas has several sales tax holidays each year. During these times, certain items are exempt from sales tax. For example:
- Back-to-School sales tax holiday (August): Exempts clothing, footwear, school supplies, and backpacks priced under $100.
- Energy Star sales tax holiday (May): Exempts qualifying Energy Star appliances such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines.
- Emergency preparation sales tax holiday (April): Exempts emergency supplies like generators, batteries, and flashlights.
Check the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts for exact dates and eligible items.
What happens if a business doesn't collect or remit Texas sales tax?
If you do not collect or remit sales tax correctly, you may face penalties and interest charges. The Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts can audit your business and impose fines, including a 10 percent penalty on unpaid taxes and interest on overdue amounts. Repeated noncompliance can lead to further penalties or suspension of your business.
What items are not subject to sales tax in Texas?
Some food items (like meat, fruits, and vegetables), prescription medications, and certain medical devices are exempt from sales tax. For more examples, check the "Sales tax exemptions in Texas" section in this guide, or visit the Texas Comptroller's website.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.
Get one month free
Sign up to any Xero plan, and we will give you the first month free.