How to measure profitability
Businesses that know how to measure profitability get better at being profitable. Find out how to do it.
Published Friday 29 September 2023
What profitability means in small business
Profitability reflects how good your business is at turning sales into profits. The main profitability metrics are your gross and net profit margins. They indicate what percentage of sales revenue you get to keep after paying business costs.
High profitability – or fat margins – mean a big chunk of your sales revenue is kept as profits, while relatively little goes back out the door to cover expenses. That’s generally a good thing but it could mean that your prices are higher than they need to be and a downward adjustment may lift sales.
Low profitability – or thin margins – means a lot of your sales revenue is used to cover business expenses. That could indicate that expenses are running high, or that your pricing is undercooked, or that you’re in a competitive market where you’re always competing on price.
Profit vs profitability and their significant differences
- Profit is the amount of money your business makes after paying its expenses.
- Profitability is the percentage of revenue you get to keep (vs the percentage that you spend to operate the business).
It’s an important distinction. High profitability only boosts your bottom line if it’s coupled with good revenue. So you want good profitability and good sales.
Profitability metrics
The most common profitability metrics are your gross and net profit margins. These are sometimes referred to as profitability ratios.
Gross profit margin
- Measures: the percentage of sales revenue remaining after paying a subset of costs known as the costs of sales. These are costs that are directly involved in providing goods or services to your customers.
- Significance: gross profit is used to pay general expenses like rent, utilities, marketing, insurance and general administration. Whatever is left after those counts as your net profit.
Net profit margin
- Measures: the percentage of sales revenue remaining after you’ve paid all business costs.
- Significance: the net profit is what the business gets to keep. It’s typically reinvested in growth or paid to owners.
Businesses may quote net profit before taxes, or after taxes. In this context, we're looking at net profit before taxes.
How to measure profitability
To measure profitability, divide profit by revenue and then multiply by 100 to get a percentage. As pre-maths, you’ll need to figure out what your profit is. This step differs between gross and net profit margin.
How to measure gross profit margin
Try our gross margin calculator.
*Net profit can be quoted before or after taxes. If quoting after-tax net profit then you need to also subtract taxes.
How to measure net profit margin
Try our net profit margin calculator.
Example of profitability measurement
A business takes 100K in sales, after spending 60K on stock and 20K on general expenses. Here are the steps to calculating the profitability metrics.
1. Gross profit = 40K
Which is 100K in revenue – 60K COS).
2. Gross profit margin = 40%
Which is 40K gross profit / 100K revenue x 100).
3. Net profit = 20K
Which is 100K revenue – 80K total costs).
4. Net profit margin = 20%
Which is 20K net profit / 100K revenue x 100).
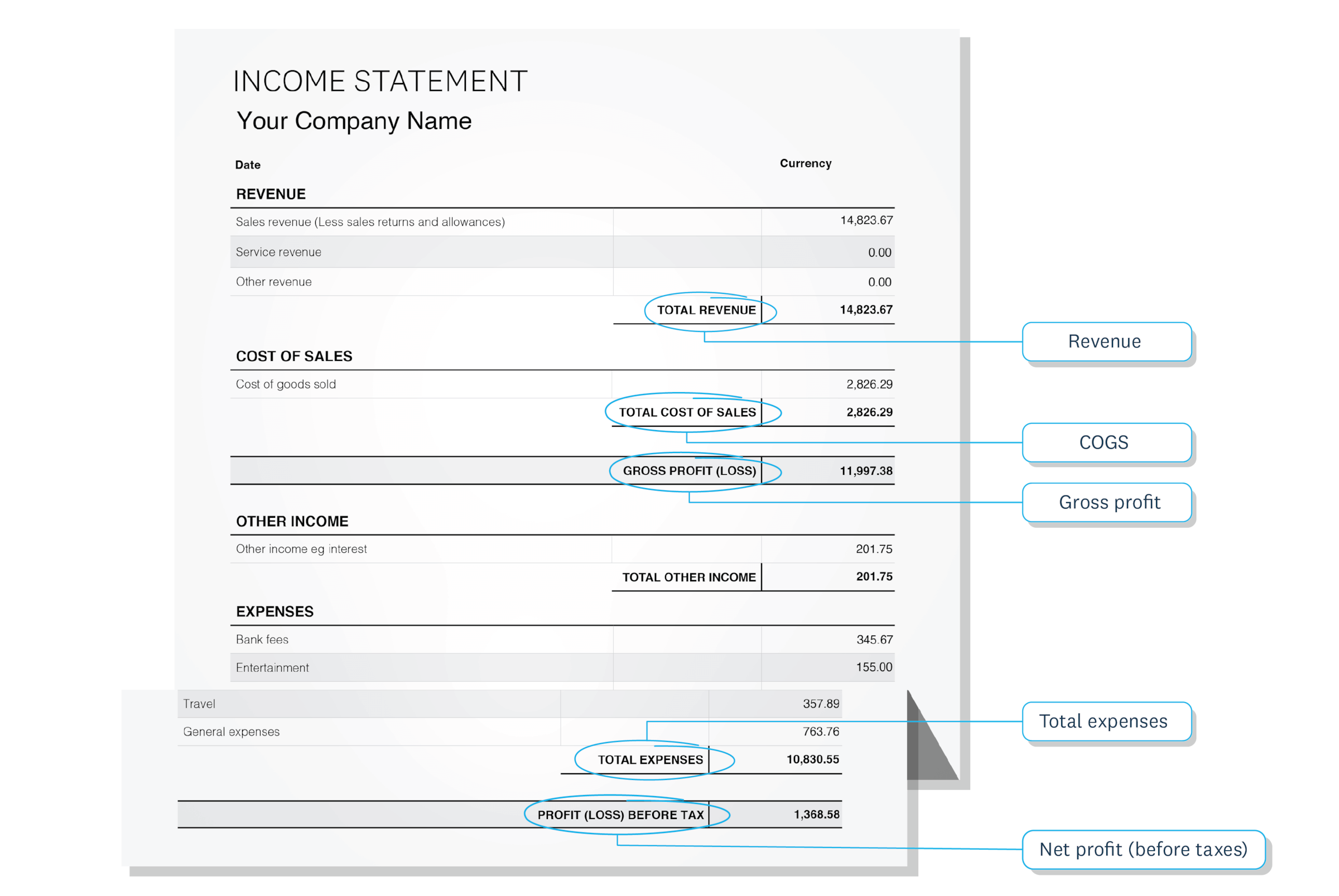
Finding the numbers to measure profitability
How to measure profitability with software
Accounting software like Xero calculates margins for you. You simply go into Xero analytics and select the period you want to measure for. Or you can generate a income statement whenever you want and do the calculation manually.
Why it’s important to keep measuring profitability
Profitability metrics like margin are key to the success of a business and the well-being of its owners. When margins get tight, cash flow typically dries up, stress goes up, and business becomes a lot less fun. Yet you want to offer good value to customers so it’s a fine balance.
Margins can change regularly due to a range of market factors such as the cost of raw materials, energy, transport, interest, rent, exchange rates and more. It’s important to keep measuring your profitability to ensure margins give you the breathing space you need.
How to manage profitability
Measure profitability regularly and especially when costs change, or if you find yourself in price wars. Find the preferred margin for your business and use that as a benchmark. Accountants or bookkeepers who work in your industry will be able to tell you what the norms are, which can also help set targets.
If they’re lower than you’d like, you can work a few levers to try and drive them up, such as increasing prices, decreasing COS, or bringing down your general expenses. Check out the tips in How to increase profits.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.
Start using Xero for free
Access Xero features for 30 days, then decide which plan best suits your business.