Profit margin: What it is, how to calculate and improve yours
See how profit margin shows what you earn on sales, and how to calculate and boost it.
Written by Jotika Teli—Certified Public Accountant with 24 years of experience. Read Jotika's full bio
Published Monday 22 December 2025
Table of contents
Key takeaways
- Calculate three distinct profit margins (gross, operating, and net)to gain comprehensive insights into different aspects of your business performance, from pricing effectiveness to overall financial health.
- Monitor profit margin trends monthly rather than focusing on single snapshots, as patterns over time reveal crucial information about operational efficiency and market positioning.
- Implement strategic cost control measures including subscription audits, vendor renegotiation, and operational efficiency improvements to directly boost your profit margins without compromising quality.
- Compare your profit margins against industry benchmarks to assess competitive positioning, as good margins vary significantly by sector, from 2-5% in retail to 20-40% in software businesses.
What is a profit margin?
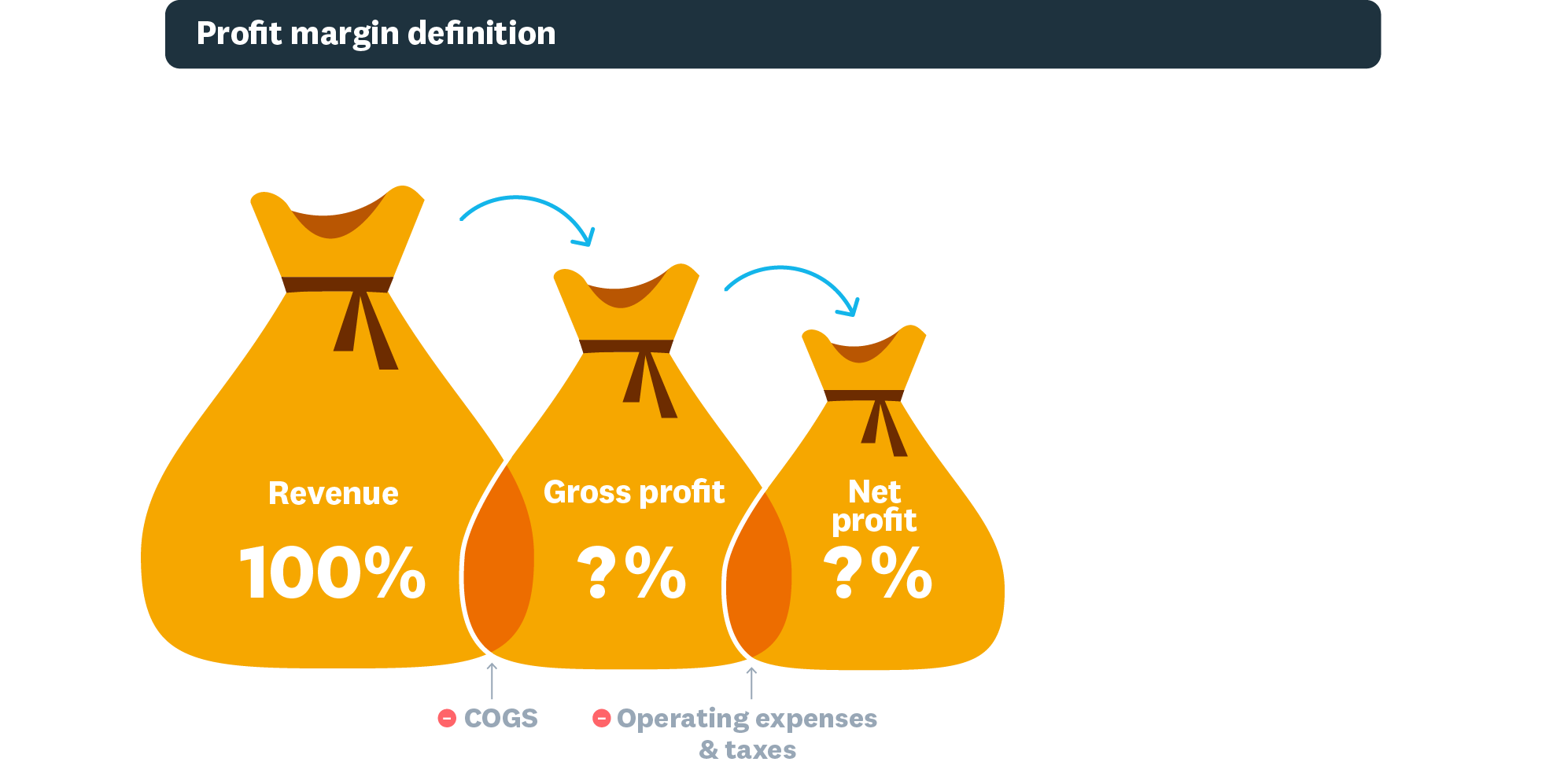
Profit margin is the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all business expenses. This metric shows how much profit your business generates for every dollar of sales.
A strong profit margin indicates financial health by showing:
- Revenue efficiency: Your business generates sufficient income to cover all expenses
- Performance insights: Clear visibility into which areas drive profitability
- Decision guidance: Data-driven direction for cost reduction and pricing strategies
Profit margins vs net profit
Net profit is the dollar amount left after expenses. Profit margin expresses this as a percentage of total revenue. For example, $10,000 profit on $50,000 revenue equals a 20% profit margin.
Types of profit margins
There are three main types of profit margins:
Gross profit margin: is your revenue minus cost of goods sold, divided by revenue
- Purpose: Set pricing and compare performance between periods
- Formula: (revenue − cost of goods sold (COGS)) ÷ revenue × 100
Operating profit margin: Profit after variable costs but before taxes and interest
- Purpose: Measure core business profitability for investors and lenders
- Formula: Operating Income ÷ Revenue × 100
Net profit margin: Income after all costs, taxes, and expenses
- Purpose: Overall financial health indicator for comprehensive analysis
- Formula: Net Income ÷ Revenue × 100
Here's more info about net profit margin.
How to calculate profit margins
Profit margin calculation follows this simple formula: (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100 = Profit Margin %
This percentage format enables easy comparison across time periods and industry benchmarks.
Gross profit margin calculation
Let's say your business makes $20,000 by cleaning offices. It costs you $8,000 to provide those services, so your gross profit is $12,000.
Therefore:
$12,000 / $20,000 x 100 = 60% gross profit margin
Try our gross profit margin calculator.
Net profit margin calculation
You also pay $4000 in taxes, so your net profit is $8000.
Therefore:
$8000 / $20,000 x 100 = 40% net profit margin
Try our net profit margin calculator.
Operating profit margin calculation
You spend another $3,000 on operating expenses, so your operating profit is $5,000.
Therefore:
$5000 / $20,000 x 100 = 25% operating profit margin
Why do profit margins matter?
Profit margins matter because they reveal critical business insights:
Financial health: Direct measure of how efficiently your business converts sales into profit
Strategic decisions: Essential data for:
- Setting competitive pricing strategies
- Identifying cost reduction opportunities
- Allocating resources for maximum return
Funding success: Banks and investors evaluate margins to assess business viability and loan risk
What is a good profit margin?
Good profit margins vary significantly by industry and business model:
- Retail: 2-5% net margin (high volume, low margin)
- Luxury goods: 15-25% net margin (low volume, high margin)
- Software: 20-40% net margin (scalable, low variable costs)
- Restaurants: 3-7% net margin (high overhead, perishable inventory)
It also depends on the type of profit margin you're considering. For instance, your gross profit margin will naturally be higher than your net profit margin as it doesn't account for all your costs. Your operating and net profit margins tell you the most crucial information about the financial health of your business.
Benefits of high profit margins for growth
High profit margins typically mean a business:
- is financially healthy, making it easier to attract investment
- has room to reinvest in its own growth
- has more space to innovate; for example, by changing pricing strategies to find a competitive edge
Have a good look at your business's performance to find trends and opportunities. It's useful to benchmark your business against your competitors to see whether you're in a strong position.
Do high profit margins guarantee growth?
Healthy margins don't guarantee growth. Yale Insights found that profit margins don't necessarily rise as businesses grow. Too-rapid growth can even eat into profit margins if your short-term costs rise. So focus on sustainable growth and consider your profit margins when you make strategic business decisions.
Factors affecting profit margins
Profit margins can vary for reasons outside your control, such as market conditions or business strategy decisions. Industries like retail stores and hospitality have naturally higher overheads than other industries, and therefore tighter profit margins than others, like business consultancies.
Economic fluctuations can greatly affect profit margins. For instance, data from the Bank of Canada shows that during the COVID-19 pandemic, nearly one in three businesses experienced a revenue drop of 30 percent or more.
Inflation and high interest rates can increase a business's costs. If you've borrowed to fund your business operations, for instance, rising interest rates will eat into your profit margins.
Your location affects the rent and taxes your business pays. Costs like these will need to be taken into account when assessing profit margins and pricing strategies.
How to increase your profit margins
Increasing profit margins requires strategic focus on three key areas that directly impact profitability:
Control your costs
Control your costs through systematic expense reduction:
- Subscription audit: Cancel unused software and services
- Labour optimization: review staffing levels and productivity metrics
- Vendor negotiation: Renegotiate contracts for better rates
- Energy efficiency: Reduce utility costs through smart usage
Make your operations more efficient
Increase your operational efficiency by delivering great customer service and encourage your team to innovate. Invest in staff training so everyone performs at their best.
Adjust your pricing
Having a strong pricing strategy that suits your industry and customers helps maximize your revenue and boost your margins. Think about:
- Dynamic pricing where you adjust prices to fit demand and seasonal changes
- Premium packages and bundles to increase revenue
Learn from high-profit-margin businesses
Certain industries have potentially higher profit margins. Factors that contribute to these higher margins are strong value propositions, operational efficiency, and customer loyalty.
Industries with high profit margins
Sectors like luxury goods, software and tech are renowned for their high profit margins. But outside these industries, some business models help companies get to healthy profit margins. Online businesses, for instance, often have higher net profit margins than bricks-and-mortar stores.
Tips for maintaining high profit margins
Even if your business isn't within a high-profit sector, or you can't change your business model, here are ways to help raise your overall profit margins that many high-profit businesses practice.
- Communicate a strong value proposition to your customers: Customers are more likely to trust a brand if they understand why they should buy from you instead of your competitor.
- Run an efficient operation: Run an efficient operation by using your resources well and cutting unnecessary costs to improve productivity and boost profit margins.
- Nurture loyal customers: A strong product, excellent customer relations, and clever marketing (such as loyalty programs) entices customers to return. Having a reliable client base can create a steadier revenue stream helping to maintain strong profit margins.
Analyze your profit margins for better business decisions
Analyze your profit margins for strategic business decisions:
- Pricing decisions: Identify products with healthy margins to guide price adjustments and product focus
- Budget creation: Allocate resources toward high-margin products and services for better return on investment (ROI)
- Investment planning: Pinpoint profitable business areas worthy of additional investment and expansion
What profit margin trends reveal
Profit margin trends are patterns in a business’s profit margins over time. They can indicate a business's financial health and operational efficiency.
For instance, a steady increase in profit margins suggests a business's financial health is improving, while an ongoing decline indicates the opposite.
There isn't a specific number that is considered a 'good' profit margin. However, comparing your profit margin trends against competitors can provide valuable insights into your business' performance in the marketplace.
Track your profit margins with the right tools
Understanding and monitoring your profit margins is essential for business success. The right accounting software automates calculations, tracks trends, and provides real-time insights into your profitability.
Xero's cloud-based platform helps you monitor profit margins and gives you the data you need to make pricing, cost management and investment decisions. Try Xero for free to see how clear financial insights can drive your business growth.
FAQs on profit margins
Here are answers to common questions about calculating and using profit margins in your business.
What does a 20% profit margin mean?
A 20% profit margin means you keep $0.20 profit for every $1.00 in sales revenue.
Is an 80% profit margin good?
An 80% profit margin is exceptionally high and whether it's 'good' depends on the context. An 80% gross profit margin might be achievable for software or digital product businesses with low production costs. However, an 80% net profit margin, after all expenses are paid, is very rare. Always compare your margins to your industry's average.
What's the difference between profit margin and markup?
Profit margin and markup both measure profitability, but they're calculated differently. Profit margin shows profit as a percentage of your revenue. Markup shows profit as a percentage of your cost. For example, if you buy a product for $50 and sell it for $100, your markup is 100% of the cost, but your profit margin is 50% of the selling price.
Can profit margins be too high?
Extremely high margins may indicate overpricing that could limit market share, but generally higher margins provide more financial flexibility.
How often should I calculate profit margins?
Calculate profit margins monthly to track trends and quarterly for strategic planning and performance reviews.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.