Profit Margin: What It Is, How to Calculate, Why It Matters
See how profit margin helps you price right, control costs, and grow profit, with simple steps to calculate it.
Written by Jotika Teli—Certified Public Accountant with 24 years of experience. Read Jotika's full bio
Published Friday 6 February 2026
Table of contents
Key takeaways
- Calculate your profit margin regularly using the formula (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100 to track your business's financial health and make informed pricing decisions.
- Focus on three key areas to improve your margins: control costs by reviewing expenses and renegotiating contracts, streamline operations through automation and staff training, and adjust pricing to reflect your value while testing customer response.
- Compare your profit margins against industry benchmarks rather than general rules, as a good margin varies significantly by sector—software companies average 19% while retail businesses often see much lower margins.
- Track margin trends over time to identify whether your financial health is improving or declining, as rising margins signal improved efficiency while falling margins indicate cost pressures or operational issues that need attention.
What is a profit margin?
Profit margin is the percentage of revenue remaining after you pay business expenses. The higher the percentage, the more profit you keep from each sale. This metric helps you understand whether your pricing covers costs and leaves room for growth.
A strong profit margin signals financial health and tells you:
- Cost coverage: Your revenue covers expenses with room to spare.
- Performance visibility: You can see which products or services generate the most profit.
- Decision support: You know where to cut costs or adjust pricing.
Profit margin vs net profit
Net profit is a dollar amount: the income left after deducting all expenses from revenue.
Profit margin is a percentage: it shows what portion of each dollar in revenue becomes profit. This makes it easier to compare performance across time periods or against other businesses, regardless of size.
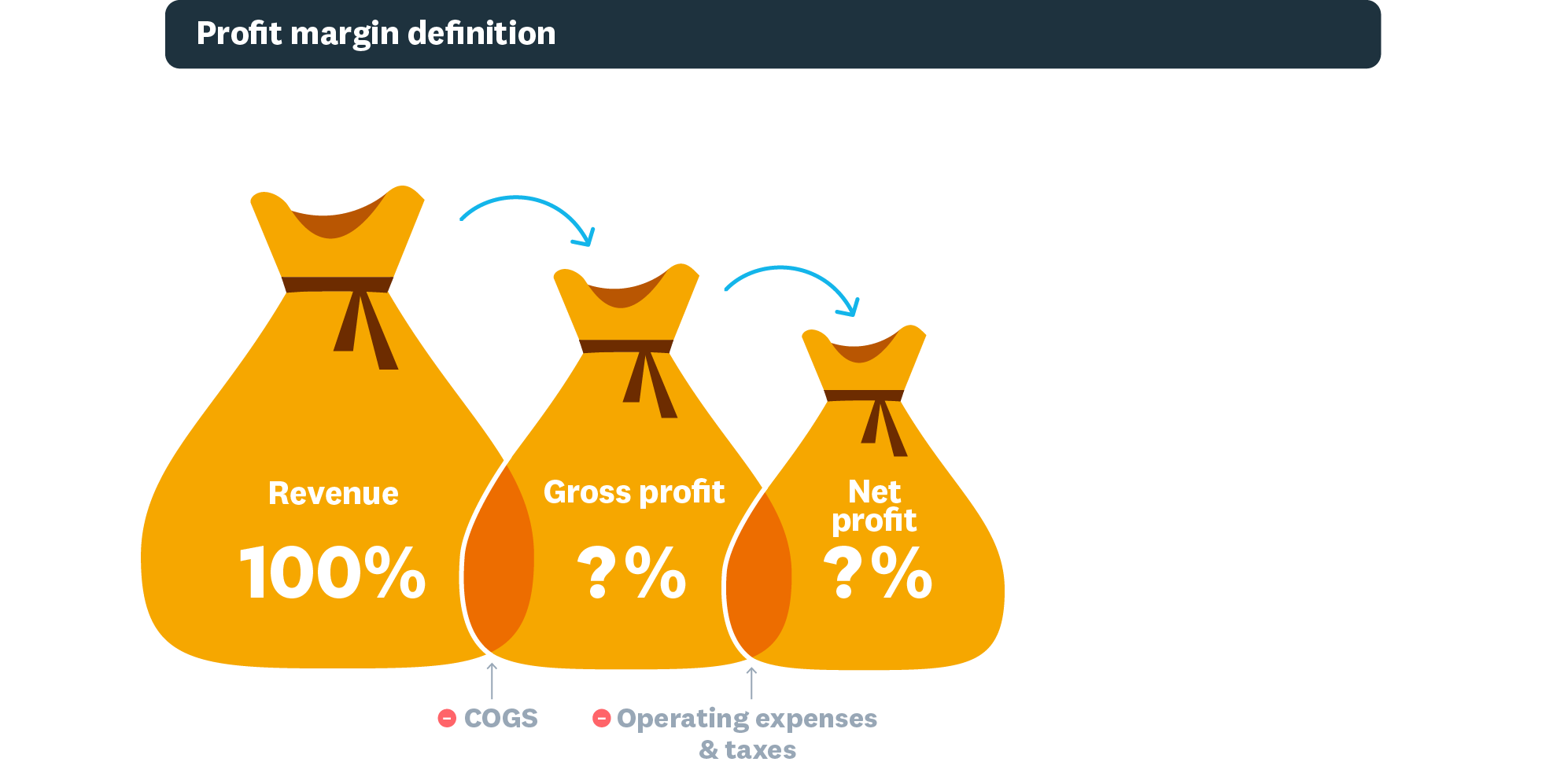
Types of profit margins
There are three main types of profit margins. Each measures profitability at a different stage of your business operations:
- Gross profit margin measures revenue remaining after paying for goods and services sold (cost of goods sold). Use it to set pricing, spot improvement areas, and compare performance between periods.
- Operating profit margin measures profit after paying variable costs like wages, materials, and operational expenses, but before taxes and interest. It shows how profitable your core operations are. Investors and lenders often review this when assessing your business.
- Net profit margin measures income remaining after paying all costs and taxes. It's the most comprehensive indicator of financial health because it accounts for every expense.
Learn more about net profit margin.
How to calculate profit margins
To calculate profit margin, use this formula:
Profit margin = (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100
This expresses your margin as a percentage, making it easy to compare across periods or against other businesses.
Gross profit margin calculation
- Calculate gross profit: Revenue minus cost of goods sold
- Divide gross profit by revenue
- Multiply by 100 to get the percentage
Example: Your cleaning business earns $20,000 in revenue. It costs $8,000 to provide those services.
- Gross profit: $20,000 − $8,000 = $12,000
- Gross profit margin: $12,000 ÷ $20,000 × 100 = 60%
Use the Xero gross profit margin calculator to run your own numbers.
Operating profit margin calculation
- Calculate operating profit: Gross profit minus operating expenses
- Divide operating profit by revenue
- Multiply by 100 to get the percentage
Example: From the $12,000 gross profit above, you spend $3,000 on operating expenses (rent, utilities, admin).
- Operating profit: $12,000 − $3,000 = $9,000
- Operating profit margin: $9,000 ÷ $20,000 × 100 = 45%
Net profit margin calculation
- Calculate net profit: Operating profit minus taxes and interest
- Divide net profit by revenue
- Multiply by 100 to get the percentage
Example: From the $9,000 operating profit, you pay $4,000 in taxes.
- Net profit: $9,000 − $4,000 = $5,000
- Net profit margin: $5,000 ÷ $20,000 × 100 = 25%
Use the Xero net profit margin calculator to calculate yours.
What is a good profit margin?
A good profit margin varies by industry, but general benchmarks can help you assess your performance:
- 5% or lower: Considered low; common in grocery and retail.
- 10%: While 10% is a common benchmark, the average net profit margin across all industries is closer to 8.54%.
- 20% or higher: Considered strong. This is typical in industries like software, where companies can see an average net profit margin of 19.14%.
Your margin also depends on which type you're measuring. Gross profit margins are naturally higher than net margins because they don't include all expenses.
Industry differences matter, so compare your margins to others in your industry for the most useful benchmark. Low-margin businesses like grocery stores rely on high sales volume. High-margin businesses like consulting firms earn more per sale but may have fewer transactions.
Why profit margins matter
Profit margins reveal your business's financial health by showing how much income you keep relative to what you spend. They help you make smarter decisions in three key areas:
- Pricing: Determine whether your prices cover costs and generate sufficient profit.
- Cost control: Identify where expenses eat into your margins.
- Resource allocation: Prioritise spending on products or services with higher returns.
You can use your margins to:
- Set prices: Identify which products deliver healthy margins and adjust pricing accordingly.
- Create budgets: Allocate resources to higher-margin products and services.
- Guide investments: Direct spending towards the most profitable parts of your business.
When you seek funding, banks and investors review your margins to assess whether your business is a sound investment, as rigorously assessing finances has been shown to reduce investment risk by 41%.
High margins create opportunities for growth:
- Attract investment: Strong margins signal financial health to lenders and investors.
- Reinvest in growth: Extra profit funds new equipment, staff, or marketing.
- Experiment with pricing: More cushion lets you test strategies without risking losses.
Compare your margins against competitors to see where you stand and spot opportunities.
Healthy margins don't guarantee growth. Research shows margins don't necessarily rise as businesses expand. Rapid growth can actually reduce margins if short-term costs spike. Focus on sustainable growth and monitor your margins as you scale.
What profit margin trends reveal
Tracking margins over time shows whether your financial health is improving or declining. Look for these patterns:
- Rising margins: Improved efficiency or successful price increases.
- Falling margins: Rising costs, pricing pressure, or operational issues.
- Stable margins: Consistent performance, though may signal missed growth opportunities.
Compare your trends against industry benchmarks and competitors to understand your position in the market.
Factors affecting profit margins
Several factors influence your margins, some within your control and some not:
- Industry type: Retail and hospitality typically have higher overheads and tighter margins than consulting or software businesses.
- Economic conditions: Inflation and rising interest rates increase costs; borrowed funds become more expensive to service.
- Location: Rent, local taxes, and regional wage expectations vary significantly and affect your cost base.
- Business model: Online businesses often achieve higher net margins than bricks-and-mortar stores due to lower overhead.
Account for these factors when setting prices and evaluating your performance.
How to increase your profit margins
To improve your margins, focus on three areas: reduce costs, improve efficiency, and adjust pricing. Here's how to tackle each.
1. Control your costs
Review expenses regularly to find savings:
- Cancel unused subscriptions and software licences.
- Renegotiate supplier contracts or find alternative vendors.
- Reduce waste in materials and inventory.
- Manage labour costs by matching staffing to demand.
2. Make your operations more efficient
Streamline how your business runs:
- Automate repetitive tasks like invoicing and data entry; research shows that using advanced analytical platforms instead of spreadsheets leads to 43% faster evaluation cycles and 28% higher forecast accuracy.
- Invest in staff training to reduce errors and rework.
- Improve customer service to increase repeat business.
- Encourage your team to suggest process improvements.
3. Adjust your pricing
Set prices that reflect your value and cover costs:
- Use dynamic pricing to adjust for demand and seasonality.
- Create premium packages or bundles to increase average sale value.
- Review competitor pricing to ensure you're positioned correctly.
- Test small price increases and monitor customer response.
- Communicate your value: help customers understand why they should choose you over competitors.
- Build customer loyalty: repeat customers provide steadier revenue and cost less to serve than acquiring new ones.
Track your profit margins with Xero
Understanding your profit margins helps you make smarter pricing decisions, control costs, and plan for sustainable growth. Tracking them regularly keeps you informed about your business's financial health.
With Xero, you get real-time visibility into your profitability through automated reporting and easy-to-read dashboards. You can monitor margins across products, services, and time periods without manual calculations.
Get started with Xero accounting software and get one month free.
FAQs on profit margins
Here are answers to common questions about profit margins.
What does a 20% profit margin mean?
A 20% profit margin means you keep $0.20 of every dollar in revenue after covering the relevant costs. For example, if you earn $100 in revenue with a 20% net profit margin, your net profit is $20.
What does a 30% profit margin mean?
A 30% profit margin means you retain $0.30 of every dollar in revenue as profit. This is generally considered a strong margin in most industries.
Can I calculate profit margin in Excel or with a calculator?
Yes. In Excel, use the formula =(Profit/Revenue)*100. You can also use the Xero gross profit margin calculator and Xero net profit margin calculator for quick calculations without setting up a spreadsheet.
How often should I calculate my profit margin?
Review your profit margins monthly at minimum. More frequent tracking, such as weekly, helps you spot issues early and respond to changes in costs or sales quickly, a practice supported by the fact that 36% of CFOs report their teams alter their forecasts at least weekly.
What's the difference between markup and profit margin?
Markup is the percentage added to your cost to set a selling price. Profit margin is the percentage of the selling price that becomes profit. A 50% markup on a $10 item means you sell it for $15. The profit margin on that sale is 33% ($5 profit ÷ $15 price).
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.