Profit margin explained: What it is, types and how to calculate
Profit margin shows how much money you keep from each sale. Learn what it is and how to calculate it.
Written by Jotika Teli—Certified Public Accountant with 24 years of experience. Read Jotika's full bio
Published Friday 7 November 2025
Table of contents
Key takeaways
• Calculate your profit margin using the formula (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100 to measure how efficiently your business converts sales into profit and track financial health over time.
• Monitor all three types of profit margins—gross, operating, and net—as each provides different insights into your business performance, with net profit margin giving the most comprehensive view of true profitability.
• Improve your profit margins by focusing on three key areas: controlling operational costs through regular expense reviews, streamlining operations for greater efficiency, and implementing strategic pricing that maximises revenue while staying competitive.
• Review your profit margins monthly and compare them against industry benchmarks to identify trends, make informed business decisions, and allocate resources toward your most profitable activities.
What is a profit margin?
Profit margin is the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all business expenses. Australian Accounting Standards define profit or loss as the total of income less expenses. It measures how efficiently your business converts sales into profit – the higher the percentage, the more money you keep. Official accounting standards require you to analyse expenses to give reliable and relevant information. Calculating your profit margin helps you do this.
A strong profit margin shows your business is financially healthy and gives you useful insights:
- Generate enough revenue to cover all costs
- Track which areas of your business are most profitable
- Identify where to reduce expenses or invest resources
Profit margins vs net profit
Net profit is the dollar amount left after paying all expenses. Profit margin is that same profit expressed as a percentage of total revenue. For example, if you earn $100,000 revenue with $20,000 net profit, your profit margin is 20%.
Types of profit margins
There are three main types of profit margin:
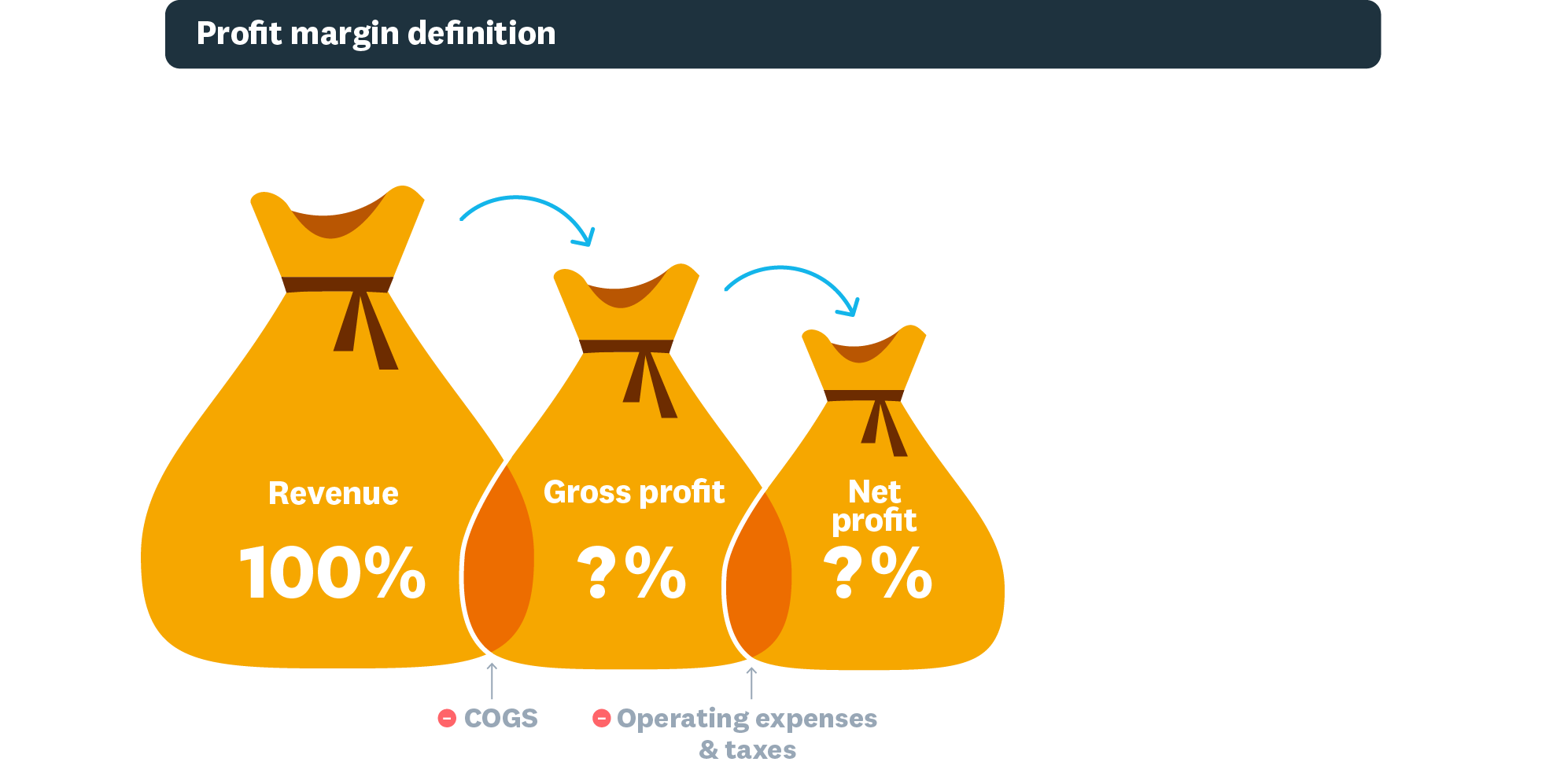
- Gross profit margin: Revenue remaining after paying for goods or services sold (cost of goods sold). This shows your core product profitability before other expenses.
- Operating profit margin: Profit after paying variable production costs like wages and materials, but before taxes and interest. This shows how efficiently you run your business.
- Net profit margin: Final profit percentage after all costs and taxes. This is your true bottom-line profitability and the most comprehensive measure of financial health.
Learn more about net profit margin
How to calculate profit margins
: (Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100 = Profit Margin %
This percentage format makes it easy to:
- Compare performance across different time periods; this practice is supported by official accounting standards that require entities to present, as a minimum, two statements of profit or loss to facilitate comparison.
- Benchmark against industry standards
- Track improvement over time
Gross profit margin calculation
Let's say your business makes $20,000 by cleaning offices. It costs you $8,000 to provide those services, so your gross profit is $12,000.
Therefore:
$12,000 / $20,000 x 100 = 60% gross profit margin
Use the Xero gross profit margin calculator.
Net profit margin calculation
You also pay $4,000 in taxes, so your net profit is $8,000.
Therefore:
$8,000 / $20,000 x 100 = 40% net profit margin
Use the Xero net profit margin calculator.
Operating profit margin calculation
You spend another $3,000 on operating expenses, so your operating profit is $5,000.
Therefore:
$5,000 / $20,000 x 100 = 25% operating profit margin
Why do profit margins matter?
Profit margins show your business’s financial health and help you make better decisions:
- Pricing strategy: Determine if your prices generate adequate returns
- Cost control: Identify areas where expenses are eating into profits
- Resource allocation: Focus investment on your most profitable activities
- Funding applications: Banks and investors use margins to assess business viability
What is a good profit margin?
Retail businesses typically see 2 – 5% net margins, while professional services often achieve 15 – 25%.
It also depends on the type of profit margin you're considering. For instance, your gross profit margin will naturally be higher than your net profit margin as it doesn't account for all your costs. Your operating and net profit margins give you the clearest picture of your business’s financial health.
Benefits of high profit margins for growth
High profit margins create growth opportunities by providing financial flexibility:
- Investment capacity: More cash available to reinvest in business expansion
- Competitive advantage: Room to adjust pricing strategies without losing profitability
- Investor appeal: Demonstrates efficient operations and strong management
Review your business’s performance to spot trends and opportunities. Benchmark your business against competitors to see how you compare.
Do high profit margins guarantee growth?
While healthy margins support growth, they do not always increase as your business grows. Yale Insights found that profit margins don't necessarily rise as businesses grow. Rapid growth can reduce profit margins if your short-term costs rise. Focus on sustainable growth and consider your profit margins when making business decisions.
Factors affecting profit margins
Profit margins can change due to market conditions or business decisions. Retail and hospitality businesses often have higher overheads and tighter profit margins than consultancies.
Economic changes can affect profit margins. Inflation and high interest rates can increase your costs. If you have business loans, rising interest rates can reduce your profit margins.
Your location affects your rent and taxes. Include these costs when you assess profit margins and set prices.
How to increase your profit margins
Increase your profit margins by focusing on three main areas:
- Cost control: Reduce operational expenses without compromising quality
- Operational efficiency: Streamline processes to deliver more value with less resource
- Strategic pricing: Optimise prices to maximise revenue while remaining competitive
1. Control your costs
Reduce operational expenses by reviewing subscriptions and removing items you no longer need. Manage your labour costs.
2. Make your operations more efficient
Improve operational efficiency by delivering great customer service, encouraging your team to innovate, and investing in staff training.
3. Adjust your pricing
Having a strong pricing strategy that suits your industry and consumer base helps maximise your revenue and, therefore, boost your margins. Think about:
- Dynamic pricing where you adjust prices to fit demand and seasonal changes
- Premium packages and bundles can increase revenue.
Learn from high-profit-margin businesses
Certain industries have potentially higher profit margins. Factors that contribute to these higher margins are strong value propositions, operational efficiency, and customer loyalty.
Industries with high profit margins
Sectors like luxury goods, software, and technology often have high profit margins. Online businesses often have higher net profit margins than bricks-and-mortar stores.
Tips for maintaining high profit margins
Even if you are not in a high-profit sector, you can still raise your profit margins by following these practices:
- Communicate a strong value proposition so customers know why they should choose you
- Streamline your operations to use resources efficiently and reduce unnecessary costs
- Build customer loyalty with a strong product, excellent service, and loyalty program
Analyse your profit margins for better business decisions
Profit margin analysis drives better business decisions across key areas:
- Pricing decisions: Identify which products or services deliver the strongest returns
- Budget planning: Allocate resources toward your most profitable activities
- Investment priorities: Focus expansion efforts on high-margin opportunities
What profit margin trends reveal
Profit margin trends are patterns in a company's profit margins over time. They can indicate a business's financial health and operational efficiency.
For instance, a steady increase in profit margins suggests a business's financial health is improving, while an ongoing decline indicates the opposite.
There is no single number for a ‘good’ profit margin. Compare your profit margin trends with competitors to see how your business is performing.
Use Xero for comprehensive profitability insights
With Xero accounting software, you can streamline your accounting processes and get real-time insights into your business’s performance and profitability.
FAQs on profit margins
Here are some common questions small business owners have about profit margins.
What does a 20% profit margin mean for my business?
A 20% profit margin means that for every dollar of revenue your business earns, you keep 20 cents as profit after all expenses have been paid. It's a clear indicator of how much of your sales revenue is converted into actual profit.
Is 80% profit margin realistic for small businesses?
An 80% gross profit margin can be realistic for some businesses, especially in service or software industries with low direct costs. However, an 80% net profit margin is very rare, as it would mean your total business expenses are extremely low. It's more helpful to compare your margins to others in your specific industry.
How do profit margins vary between industries?
Profit margins differ greatly across industries. For example, retail businesses often have lower margins due to the high cost of goods, while software or consulting businesses may have higher margins because their direct costs are lower. What's considered a 'good' margin in one industry might be low in another.
What's the difference between gross and net profit margin in simple terms?
Gross profit margin shows the profit you make just from selling your product or service, before considering your general business operating costs. Net profit margin shows your final profit after all expenses, including operating costs, interest, and taxes, have been deducted. Net profit margin gives you the complete picture of your business's profitability.
How often should I calculate my profit margins?
It's a good practice to review your profit margins monthly. Regular tracking helps you spot trends, understand the impact of your business decisions, and make timely adjustments to pricing or costs. Using accounting software can make this a quick and simple part of your monthly financial check-in.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.