How to calculate break-even point
November 2023 | Published by Xero
Break-even point formula (calculation)
Break-even point is business costs divided by sales prices. The results show what level of sales are needed for a business to become profitable.
To calculate the break-even point, you can use two formulas:
- Revenue break-even formula: Calculates the total value of sales (revenue) required to break even.
- Volume break-even formula: Determines the number of sales (volume) required to cover costs.
What is the break-even point?
Break-even point shows when a business can successfully cover its costs. It’s a big milestone because that’s the point at which a business becomes profitable. These calculations are often used to help set baseline productivity and sales targets..
Revenue break-even point formula
Revenue break-even formula is easier to calculate. It gives you a monetary figure that you need to beat to be profitable.
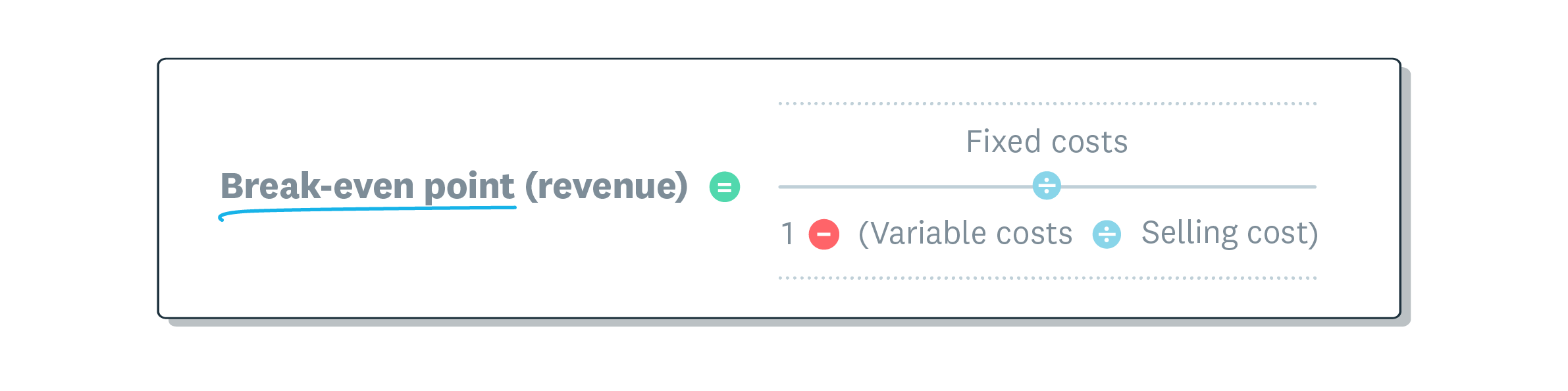
How to calculate revenue break even point
Where:
- Break even point (revenue) is the dollar value of sales required to reach profitability
- Fixed costs: expenses that stay the same no matter how much business you’re doing. They include things like rent, insurance, and so on
- Variable costs: are expenses that change with production volume. They include things like raw materials, or hourly wages
- Selling price: what you charge for your goods or services
Volume break-even point formula
Volume break-even formula tells you how much work you need to do to break even. It’s a simple calculation for businesses that sell one type of product, or service businesses that have a single hourly rate. But it gets tricky if you sell lots of things at different prices.

How to calculate volume break even point
Examples of calculating the break-even point
Check out these break-even calculation examples for product-based and service-based businesses. The revenue and volume break-even point is shown for each.
Break-even example for a product-based business
A kombucha brewery:
- Fixed costs: $6,000 per month (e.g., rent, utilities, advertising)
- Variable costs: $2 per bottle (packaging, ingredients, labour)
- Selling price: $7 per bottle
Revenue required = Fixed Costs / 1 – (Variable Costs / Selling Price)
$6,000 / 1 – ($2 / $7)
= $8,403
To break even, the kombucha brewery must bring in $8,403 monthly.
Volume required = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price – Variable Costs)
$6,000 / ($7 - $2)
= 1,200
To break even, the kombucha brewery must sell 1,200 bottles monthly.
Break-even example for a service-based business
A graphic designer:
- Fixed costs: $2,700 per month (e.g., subscriptions, utilities, advertising)
- Variable costs: $35/hour (contractor fees)
- Selling price: $75/hour
Revenue required = Fixed Costs / 1 – (Variable Costs / Selling Price)
$2,700 / 1 – ($35 / $75)
= $5,064
To break even, the graphic designer must earn $5,064 monthly.
Volume required = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price – Variable Costs)
$2,700 / ($75 - $35)
= 67.5
To break even, the graphic designer must bill 67.5 hours monthly.
See related terms
Handy resources
Advisor directory
You can search for experts in our advisor directory
How to increase revenue
Find out how businesses grow their sales income.
Stay on top of your numbers with Xero
Accounting software tracks your performance while you sleep.
Disclaimer
This glossary is for small business owners. The definitions are written with their requirements in mind. More detailed definitions can be found in accounting textbooks or from an accounting professional. Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice.