What is break-even point formula? Definition and FAQs
Calculating your break-even point helps you understand when your business starts making profit.
November 2023 | Published by Xero
Published Monday 13 October 2025
Table of contents
Key takeaways
• Calculate your break-even point using the revenue formula (fixed costs ÷ [1 - (variable costs ÷ selling price)]) to determine the exact dollar amount of sales needed to cover all business costs.
• Separate your business expenses into fixed costs (rent, insurance, subscriptions) and variable costs (materials, packaging, direct labour) to ensure accurate break-even calculations and better cost management.
• Use break-even analysis to test different business scenarios, such as price changes or marketing campaigns, helping you make proactive decisions about pricing strategies and sales targets.
• Recalculate your break-even point whenever costs or prices change significantly, and review it quarterly or annually to maintain realistic financial goals and track business progress.
Break-even point definition
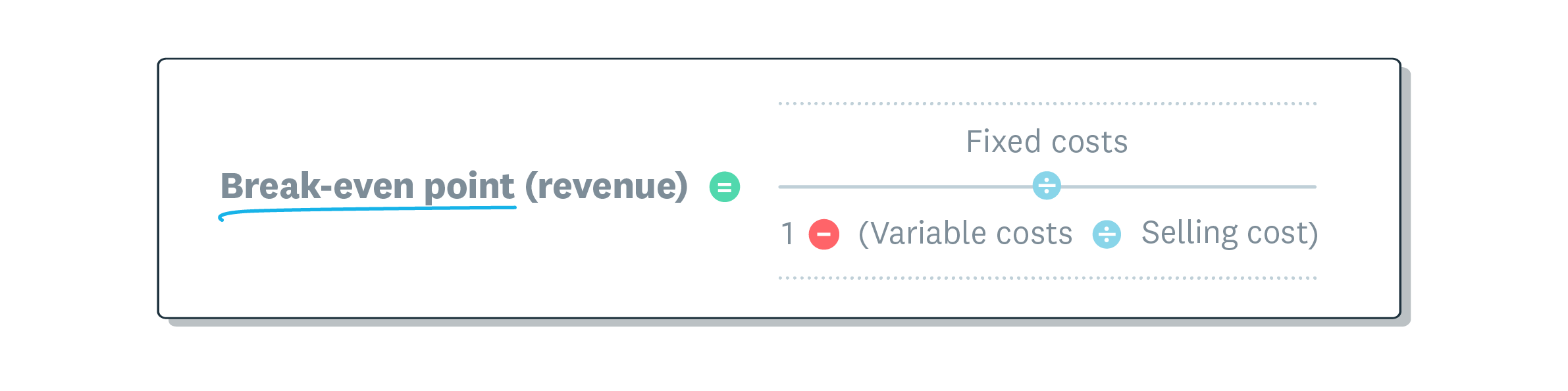
How to calculate revenue break even point
Break-even point is the exact sales level where your business covers all costs without making a profit or loss. This milestone marks when your business transitions from losing money to becoming profitable. Use break-even calculations to set realistic sales targets and understand the minimum performance needed for sustainability.
Why break-even point matters for your business
Knowing your break-even point helps you make confident decisions for your business. It gives you a clear financial target to aim for, taking the guesswork out of your planning.
You can use it to:

How to calculate volume break even point
- Set smart pricing for your products or services
- Create realistic sales goals for your team
- Understand the impact of your costs and find ways to be more efficient
- Show potential lenders or investors that your business is viable
Knowing your break-even point helps you take the first step towards making a profit.
Understanding your costs
To calculate your break-even point, first understand the two types of costs in your business.
- Fixed costs: These are expenses that stay the same each month, such as rent, insurance and software subscriptions.
- Variable costs: These costs go up or down depending on your sales volume. They include raw materials, packaging and direct labour.
Separating these costs is key to getting an accurate break-even calculation.
Break-even point formula (calculation)
The break-even point shows the sales volume or revenue needed to cover all business costs. You can calculate it in two ways:
- Revenue break-even: Shows the dollar amount of sales needed
- Volume break-even: Shows the number of units you need to sell
Revenue break-even point formula
Revenue break-even formula calculates the total dollar value of sales required to cover all business costs. This approach is simpler for most businesses because it gives you a clear sales target.
How to calculate revenue break-even point
Key formula components:
- Break-even point (revenue): the sales amount you need to cover all costs
- Fixed costs: expenses that stay the same each month, such as rent, insurance and salaries
- Variable costs: expenses that change with production, such as raw materials, hourly wages and packaging
- Selling price: the amount you charge per unit or service
Volume break-even point formula
Volume break-even formula calculates the number of units or hours you need to sell to cover costs.
This formula works best for:
- Single-product businesses: Companies selling one main product
- Service businesses: Those charging a consistent hourly rate
- Simple pricing models: Businesses with uniform pricing
This method is more complex if you sell multiple products at different prices.
How to calculate volume break even point
Examples of calculating the break-even point
Here are examples of how to calculate break-even point for different business types.
Break-even example for a product-based business
Kombucha brewery example:
- Fixed costs: $6,000 per month (rent, utilities, advertising)
- Variable costs: $2 per bottle (packaging, ingredients, labour)
- Selling price: $7 per bottle
Revenue calculation:
$6,000 ÷ [1 – ($2 ÷ $7)] = $8,403 monthly revenue needed
Result: The kombucha brewery must generate $8,403 in monthly sales to break even.
Volume calculation:
$6,000 ÷ ($7 – $2) = 1,200 bottles monthly
Result: The kombucha brewery must sell 1,200 bottles per month to break even.
Break-even example for a service-based business
Graphic designer example:
- Fixed costs: $2,700 per month (subscriptions, utilities, advertising)
- Variable costs: $35 per hour (contractor fees)
- Selling price: $75 per hour
Revenue required = Fixed Costs / 1 – (Variable Costs / Selling Price)
$2,700 / 1 – ($35 / $75)
= $5,064
To break even, the graphic designer must earn $5,064 monthly.
Volume required = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price – Variable Costs)
$2,700 / ($75 - $35)
= 67.5
To break even, the graphic designer must bill 67.5 hours monthly.
Using break-even analysis in your business
Use your break-even point to guide your business strategy. For example, what happens if you increase your prices? How would a new marketing campaign affect your profit?
Use your break-even analysis to test different scenarios and see how changes in costs or sales could affect your profit. It helps you make proactive decisions, so you can plan for growth.
Take control of your business finances with Xero
Calculating your break-even point is easier when your financial data is organised and up to date. Xero gives you a real-time view of your income and expenses, so you always know where your business stands.
Track your progress, make informed decisions and focus on what you do best. Start your free trial with Xero.
FAQs on break-even point
Here are answers to some common questions about break-even point.
What's the difference between break-even point and profit?
Your break-even point is where your total revenue equals your total costs – you haven't made or lost money. Profit is the money you make after you've passed your break-even point and covered all your costs.
How often should I recalculate my break-even point?
It's a good idea to recalculate your break-even point whenever your costs or prices change significantly. Reviewing it quarterly or annually can also help you stay on top of your financial goals.
What if I sell multiple products at different prices?
If you sell multiple products, you can calculate an average break-even point. You'll need to determine the sales mix (the percentage of total sales each product represents) and use a weighted average contribution margin in your formula.
Can my break-even point change?
Yes, it can. Your break-even point will change if your fixed costs, variable costs, or selling prices change. For example, if your rent increases, you'll need to sell more to break even.
What should I do once I reach my break-even point?
Reaching your break-even point is a great milestone. The next step is to focus on generating a profit. You can do this by increasing sales, managing your costs, or adjusting your pricing strategy. It's time to set new goals for growth.
Handy resources
Advisor directory
You can search for experts in our advisor directory
How to increase revenue
Find out how businesses grow their sales income.
Stay on top of your numbers with Xero
Accounting software tracks your performance while you sleep.
Disclaimer
This glossary is for small business owners. The definitions are written with their requirements in mind. More detailed definitions can be found in accounting textbooks or from an accounting professional. Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice.