What is profit margin and how to calculate it
Learn what a profit margin is, how to calculate it, and what it means for your business.
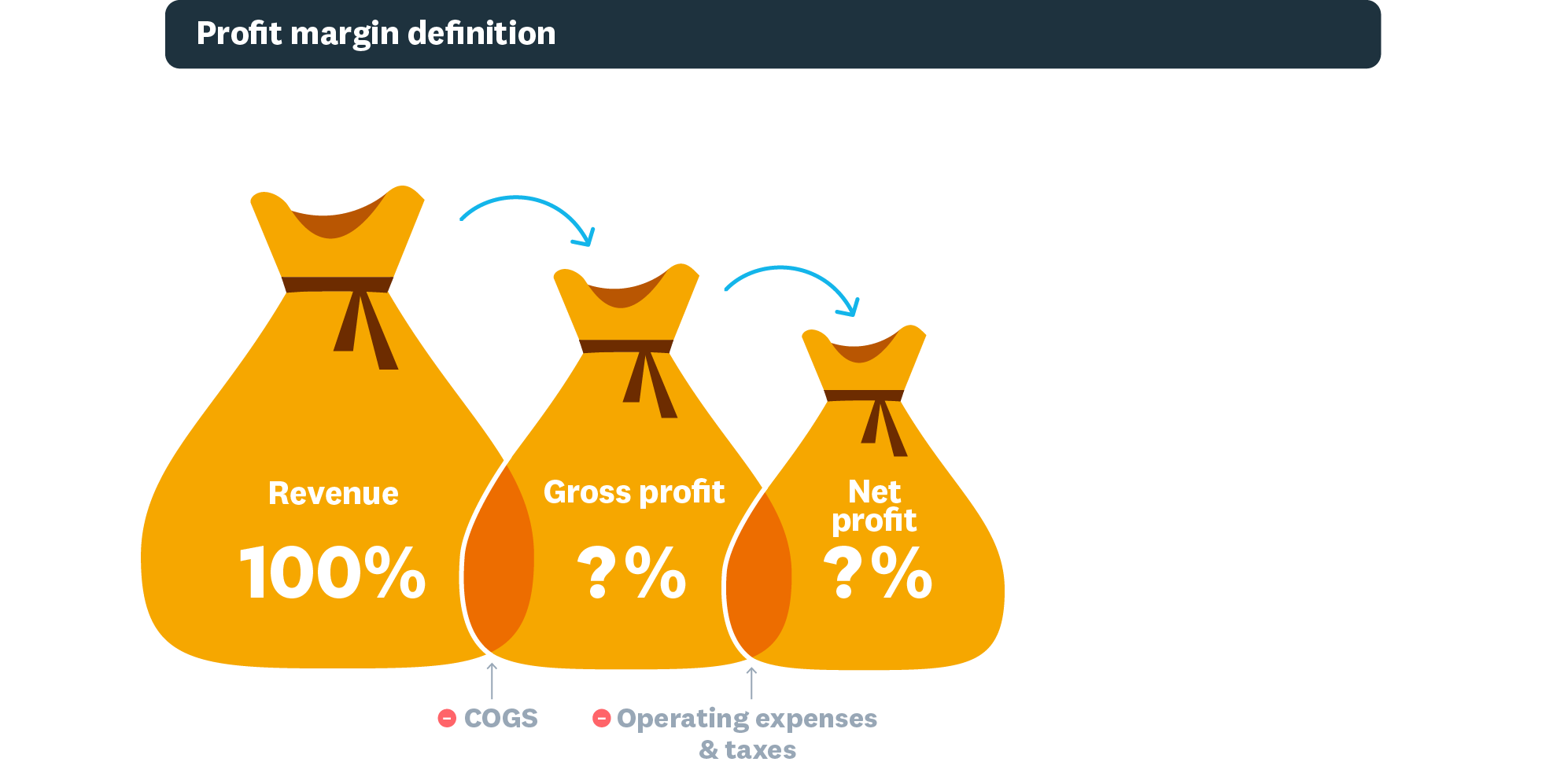
What is a profit margin?
A profit margin is the percentage of revenue left after paying business expenses. The higher the percentage, the greater the profit left over.
A strong profit margin means your business is making enough revenue to cover its costs. Your profit margin shows you where your business is performing well and helps you decide where you need to cut costs.
Profit margins vs net profit
Net profit is the actual amount of income that remains after deducting expenses from your revenue . But your profit margin is the proportion of your profit (as a percentage) of your revenue over your expenses. It shows you how much profit the business has generated while considering how much it has spent.
Types of profit margins
There are three main types of profit margins:
- Gross profit margin is the proportion of revenue left after paying for the goods and services you sell (your cost of goods sold) divided by your gross revenue. This amount is then multiplied by 100% to calculate your gross profit margin. You use the gross profit margin to set pricing, identify areas for improvement, and compare performance between periods.
- Operating profit margin is your profit after paying for variable costs of production (like wages, operational costs, and materials), but before paying taxes and interest. Operating profit margins show how profitable a business is within its core operations, with higher ratios showing better performance. Investors and lenders often use it to decide if a business is a sound investment.
- Net profit margin is the ratio of income left after paying all costs and taxes over the total revenue of the business. It’s one of the most important indicators of a business’s financial health because it accounts for all costs and expenses.
How to calculate profit margins
To calculate each profit margin, divide the amount of profit by the revenue, and multiply by 100. This expresses the profit margin as a percentage, which makes it easier to compare between accounting periods or businesses.
Gross profit margin calculation
Let’s say your business makes $20,000 by cleaning offices. It costs you $8,000 to provide those services, so your gross profit is $12,000.
Therefore:
$12,000 / $20,000 x 100 = 60% gross profit margin
Try our gross profit margin calculator.
Net profit margin calculation
You also pay $4000 in taxes, so your net profit is $8000.
Therefore:
$8000 / $20,000 x 100 = 40% net profit margin
Try our net profit margin calculator.
Operating profit margin calculation
You spend another $3,000 on operating expenses, so your operating profit is $5,000.
Therefore:
$5000 / $20,000 x 100 = 25% operating profit margin
Why do profit margins matter?
Profit margins are a sign of your business’s financial health as they show your income in relation to your expenses. They provide information to assist the business in making decisions on pricing, controlling costs, and budgeting and allocating resources. And when your business needs funding, banks and investors will scrutinise your margins when making a decision.
What is a good profit margin?
A ‘good’ profit margin depends on your industry and business type. For instance, low-end retail often has high sales but low profit margins, while luxury retail has lower turnover but higher margins.
It also depends on the type of profit margin you’re considering. For instance, your gross profit margin will naturally be higher than your net profit margin as it doesn’t account for all your costs. Your operating and net profit margins tell you the most crucial information about the financial health of your business.
Benefits of high profit margins for growth
High profit margins typically mean a business:
- Is financially healthy, making it easier to attract investment
- Has room to reinvest in its own growth
- Has more space to innovate – for example, by changing pricing strategies to find a competitive edge
Have a good look at your business’s performance to find trends and opportunities. It’s useful to benchmark your business against your competitors to see whether you’re in a strong position.
Do high profit margins guarantee growth?
Healthy margins don’t guarantee growth. Yale Insights found that profit margins don’t necessarily rise as businesses grow. Too-rapid growth can even eat into profit margins if your short-term costs rise. That’s why it’s important to prioritise sustainable growth and to consider your profit margins when making strategic business decisions.
Factors affecting profit margins
Profit margins can vary for reasons outside your control, such as market conditions or business strategy decisions. Industries like retail stores and hospitality have naturally higher overheads than other industries, and therefore tighter profit margins than others, like business consultancies.
Economic fluctuations can greatly affect profit margins. Inflation and high interest rates can increase a business’s costs. If you’ve borrowed to fund your business operations, for instance, rising interest rates will eat into your profit margins.
Your location affects the rent and taxes your business pays. Costs like these will need to be taken into account when assessing profit margins and pricing strategies.
How to increase your profit margins
To boost your profit margins, you’ll need to focus on the three main contributors: costs, operational efficiency, and pricing.
Control your costs
Look to reduce operational expenses, such as by reviewing subscriptions to remove items no longer needed and managing labour costs.
Make your operations more efficient
Increase your operational efficiency by delivering great customer service and encourage your team to innovate. Invest in staff training so everyone performs at their best.
Adjust your pricing
Having a strong pricing strategy that suits your industry and consumer base helps maximise your revenue and, therefore, boost your margins . Think about:
- Dynamic pricing where you adjust prices to fit demand and seasonal changes
- Premium packages and bundles can increase revenue.
Learn from high-profit-margin businesses
Certain industries have potentially higher profit margins. Factors that contribute to these higher margins are strong value propositions, operational efficiency, and customer loyalty.
Industries with high profit margins
Sectors like luxury goods, software and tech are renowned for their high profit margins. But outside these industries, some business models help companies get to healthy profit margins. Online businesses, for instance, often have higher net profit margins than bricks-and-mortar stores.
Tips for maintaining high profit margins
Even if your business isn’t within a high-profit sector, or you can’t change your business model, here are ways to help raise your overall profit margins that many high-profit businesses practice.
- Communicate a strong value proposition to your customers: Customers are more likely to trust a brand if they understand why they should buy from you instead of your competitor.
- Run an efficient operation: Streamlining your operations by efficiently utilising your resources and reducing unnecessary costs improves productivity and boosts profit margins.
- Nurture loyal customers: A strong product, excellent customer relations, and clever marketing (such as loyalty programmes) entices customers to return. Having a reliable client base can create a steadier revenue stream helping to maintain strong profit margins.
Analyse your profit margins for better business decisions
Use your profit margin data to:
- Decide on pricing: profit margin data helps you identify the products that deliver healthy margins over the costs associated with those products. The result of this margin will help you re-evaluate and adjust your prices
- Create a budget: understanding your profit margins helps you prioritise your resources towards products or services that deliver higher margins, and therefore provide a better return on investment
- Make investment decisions: profit margins show you where the most profitable parts of your business are
What profit margin trends reveal
Profit margin trends are patterns in a company’s profit margins over time. They can indicate a business’s financial health and operational efficiency.
For instance, a steady increase in profit margins suggests a business’s financial health is improving, while an ongoing decline indicates the opposite.
There isn’t a specific number that is considered a ‘good’ profit margin. However, comparing your profit margin trends against competitors can provide valuable insights into your business’ performance in the marketplace.
Use Xero for comprehensive profitability insights
Xero helps you streamline your accounting processes, and gives you real-time insights into your business’s performance and profitability.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.